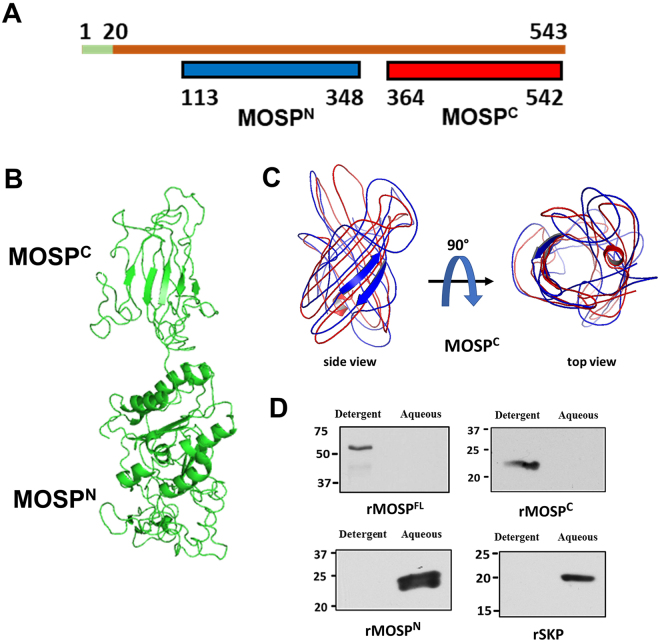
Figure 1.
MOSPFl contains N- and C-terminal domains with different solubility properties. (A) Domain architecture of MOSPFl predicted by InterProScan. The first 20 amino acids (shown in green) contain the cleaved signal sequence. The portion of MOSPFl colored in blue denotes the N-terminal domain, MOSPN, while red denotes the C-terminal domain, MOSPC. (B) Optimal model for MOSPFl, generated by I-TASSER, predicting a bipartite architecture in which MOSPN, contains substantial α-helical content and MOSPC is predominantly β-sheet. (C) Overlay of models generated by I-TASSER predicting that MOSPC is a 10-stranded β-barrel. (D) 10 µg of recombinant MOSPFl, MOSPC, MOSPN and Skp were phase-partitioned in TX-114 and separated on SDS-PAGE. Lanes show detergent-enriched and aqueous phases probed with antisera directed against each recombinant protein. Panel D presents cropped images; the full-length images are presented in Supplementary Figure 4.