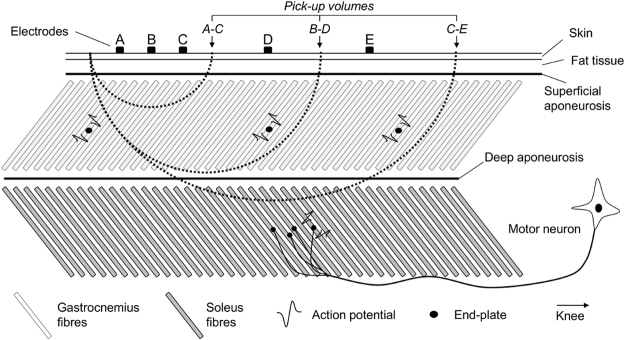
Figure 1.
Pick-up volume and inter-electrode distance. A schematic representation of the tissue volume sampled by pairs of electrodes with different inter-electrode distances is shown. Dashed lines indicate the pick-up volume of individual pairs of electrodes; i.e., the region within which action potentials contribute substantially to the surface EMGs. By substantially we mean the amplitude of action potentials within the pick-up volume is at least 10% of that of action potentials located immediately below the recording electrodes14,31. Note the number of gastrocnemius fibres included in the pick-up volume increases with the inter-electrode distance. Surface EMGs detected by electrodes A and C sample predominantly from the most distal gastrocnemius fibres; unrepresentative muscle sampling. By increasing the inter-electrode distance (electrodes B-D), surface EMGs sample from more proximal gastrocnemius fibres. After a certain distance (cf. electrodes C-E in Fig. 1), fibres from the deep, soleus muscle are expected to contribute substantially to the surface EMG; EMGs are not specific for gastrocnemius.