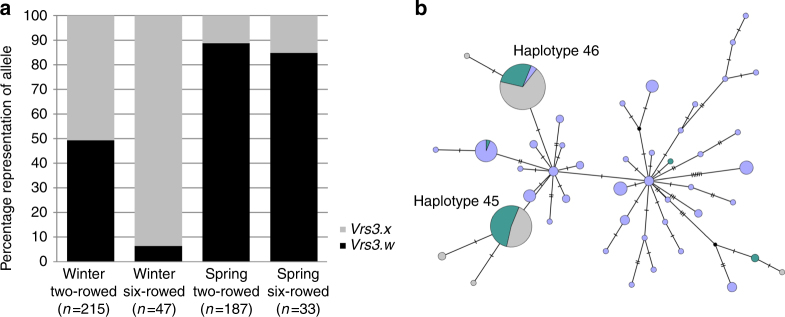
Fig. 3.
The allelic diversity of VRS3 across wild, landrace and cultivated barley germplasm. a Frequency of Vrs3.w and Vrs3.x alleles across the major classification divisions (winter-sown, spring-sown, two-rowed and six-rowed) within cultivated barley. b Median joining network illustrating the occurrence and relationships between different Vrs3 haplotypes across wild species (purple), two-rowed landrace (green) and six-rowed landrace (grey) germplasm. Tick marks across the connecting bars represent the number of polymorphisms distinguishing haplotype groups. The size of the circle is proportional to the number of representatives within the allelic class. Vrs3.w and Vrs3.x are renamed haplotype 45 and 46 because three SNPs at the 5′ and 3′ end of the exome capture alignments were missing from the alignment