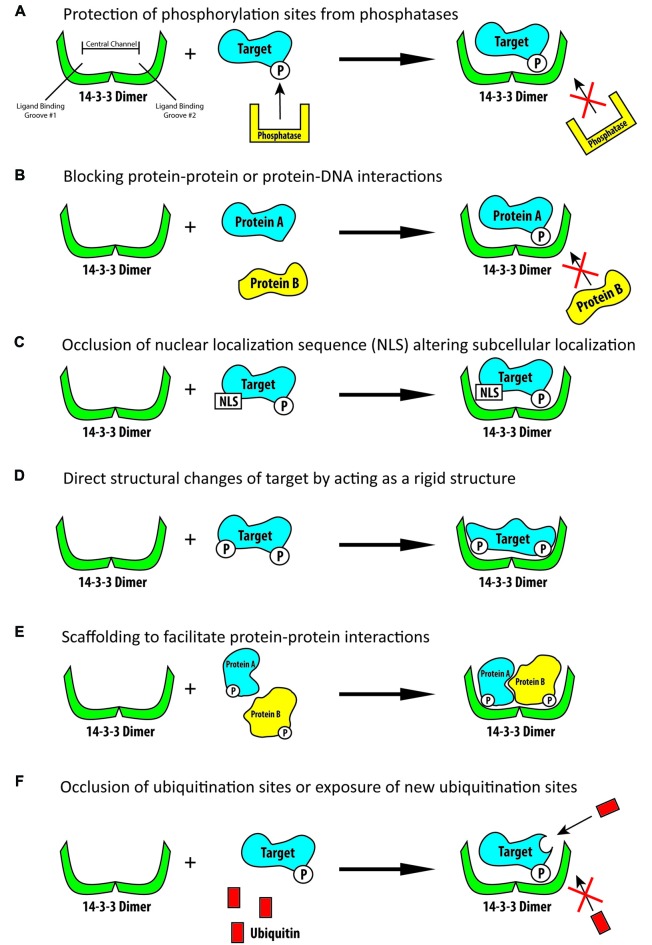
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of some of the known functions of 14-3-3 proteins. (A) 14-3-3 proteins are able to bind phosphorylated targets and prevent their dephosphorylation by phosphatases. (B) 14-3-3 proteins can bind phosphorylated targets and block protein-protein or protein-DNA interaction sites. (C) 14-3-3 proteins are able to bind their targets and block localization signals, including nuclear localization signals, thus altering their targets subcellular localization. (D) 14-3-3 proteins can produce direct conformational changes on their targets by acting as rigid structures. (E) 14-3-3 proteins can act as rigid scaffolding structures and bind multiple targets to bring them into close proximity to one another. (F) 14-3-3 proteins can bind their target and block ubiquitination sites thus preventing the subsequent degradation of their target or they may bind their target and increase ubiquitination and subsequent degradation.