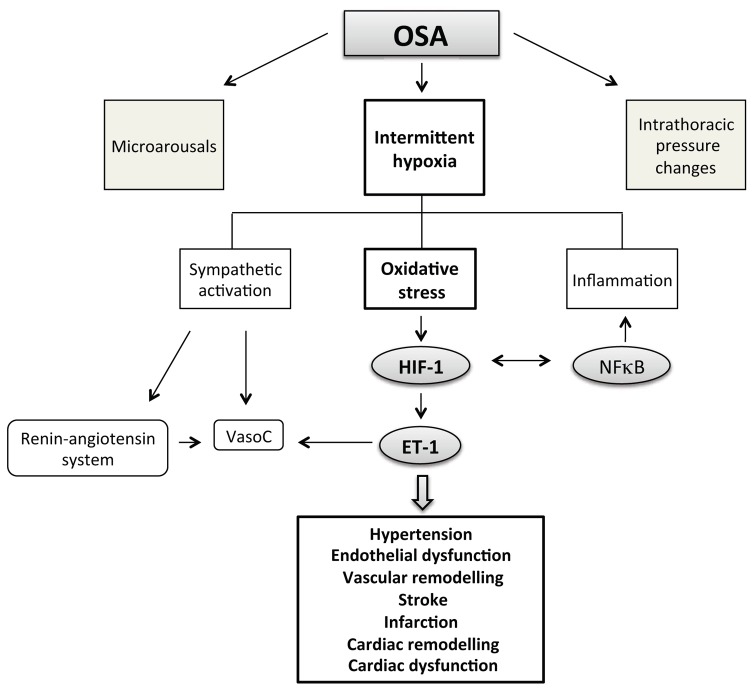
Fig. 1.
Among the consequences of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), intermittent hypoxia plays a major role in the development of associated cardiovascular pathologies. More specifically, intermittent hypoxia is well recognized to induce oxidative stress with subsequent activation of the hypoxia inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) transcription factor and upregulation of genes deleterious for the cardiovascular system such as the endothelin-1 (ET-1) gene. NFκB, nuclear factor kappa B; VasoC, vasoconstriction.