Figure 7.
Pairwise Correlations Carry More Information to Natural Odors
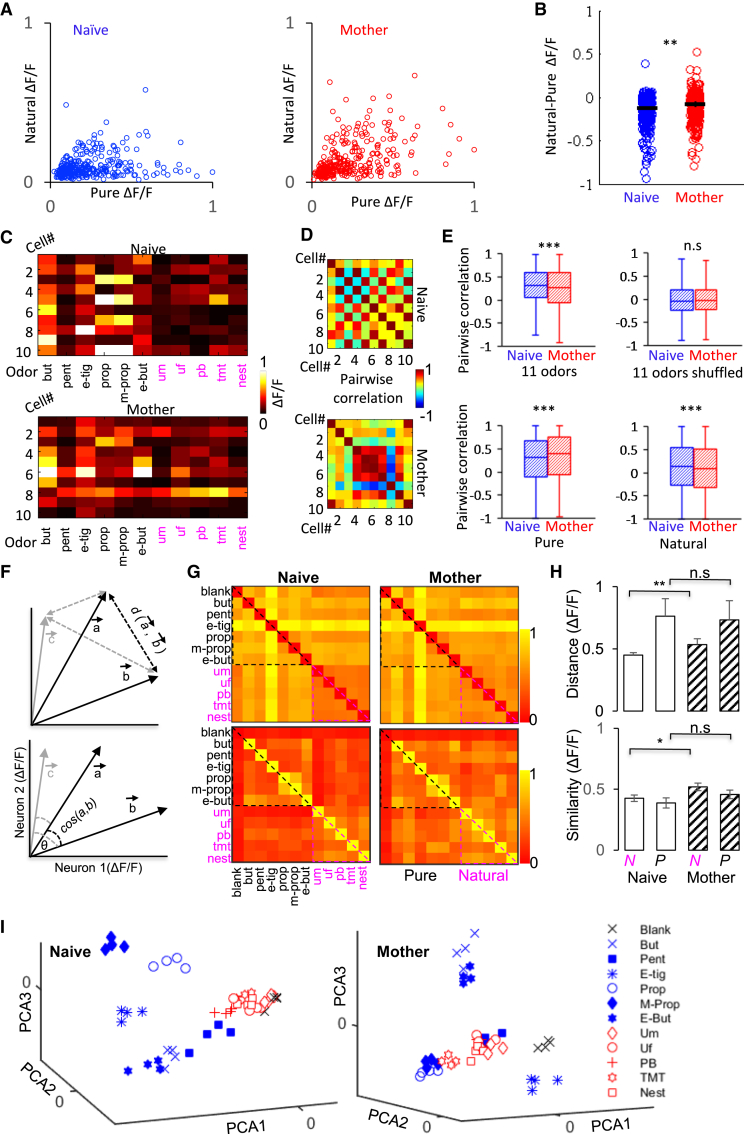
(A) Scatterplots of maximum response amplitudes in individual MCs responding to both natural and pure odors, normalized to the maximum response. Blue, naive females; red, mothers.
(B) Scatterplot of the difference in calcium response to natural and pure odors in all cells responding both to pure and natural odors (∗∗p < 0.001, Mann-Whitney U test). The line marks the mean ± SEM.
(C) Ten MCs and their maximum response to all 11 odors presented (pure + natural) from the same recorded field. Top, naive female; bottom, mother.
(D) Pairwise correlation matrices from the representative MCs in (C).
(E) Mean pairwise correlation for all odors together, all odors shuffled, only pure odors, and only natural odors, respectively. ∗∗∗p < 0.0001, Mann-Whitney U test. For each box, the central mark indicates the median and the bottom and top edges indicate the 25th and 75th percentiles, respectively. The whiskers extend to the most extreme data points.
(F) Diagrammatic representation of how population response profiles were analyzed. For simplification, a network comprised of only 2 neurons is shown (all neurons were used for each odor response vector in our analysis). Each response to a given odor (here, a, b, c, etc.) was plotted as a vector of the calcium response magnitude of all responsive neurons (neuron 1, neuron 2, etc.). When the vector for a given odor was constructed, the Euclidean distance (d, top) and cosine similarity (cos, bottom) between all pairs of vectors was calculated (here, cos/d(a,b), cos/d(a,c), and cos/d(b,c) are shown in gray).
(G) Each matrix shows all pairwise distances between all odors in both groups (mothers, n = 78 pairs from 4 mice; naive females, n = 78 pairs from 4 mice). Dotted lines denote the pairwise comparisons restricted to pure odors (blue dotted line) and those restricted to natural odors (magenta dotted line). Top: Euclidean distance; bottom, cosine similarity. Odors: butanal (but), pentanal (pent), ethyl tiglate (e-tig), propanal (prop), methyl propionate (m-prop), ethyl butyrate (e-but), male urine (Um), female urine (Uf), peanut butter (PB), TMT, nest bedding + pup (nest).
(H) The pairwise similarities and pairwise distances among pure odors are not significantly different between naive females and mothers (Wilcoxon rank-sum test; distance, p = 0.8; similarity, p = 0.11). The pairwise similarities and distances among natural odors are significantly higher in mothers compared with naive females (Wilcoxon rank-sum test; distance, ∗∗p = 2.4e−04; similarity, ∗p = 0.038).
(I) Principal-component analysis (PCA) showing the three first PCAs for all odors (n = 11 odors + blank) and all trials (n = 4) pooled across MCs of all animals per group. Left, naive females; right, mothers.