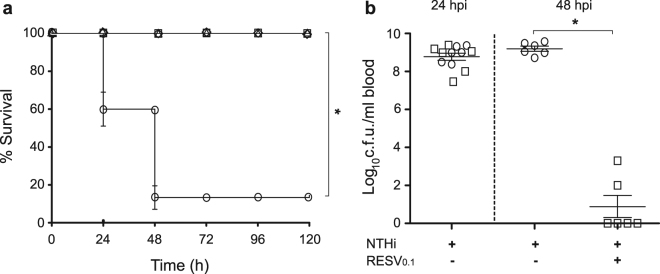
Figure 5.
Effect of resveratrol administration on zebrafish infected by NTHi. Zebrafish were infected intraperitoneally with ∼5×107 bacteria/individual. When necessary, resveratrol 0.1 mg/g/dose (RESV0.1) was administered intraperitoneally at 29 and 53 hpi. (a) Effect of resveratrol administration on adult zebrafish survival upon NTHi375 infection. Non-infected groups were administered perfusion solution-DMSO (1:1) (triangle) or saline solution 0.9% (diamond); infected groups were administered perfusion solution-DMSO (1:1) (circle) or resveratrol (square). Survival rate is reported as percentage (mean ± SD) of adult individuals survival at 120 hpi. Survival of NTHi infected zebrafish was significantly higher in resveratrol treated- and in untreated animals (p < 0.0001). (b) Bacterial counts on zebrafish blood samples from the caudal fin were determined at 24 and 48 hpi (log10 c.f.u./ml blood), corresponding to 5 h before- and 19 h post-resveratrol treatment, respectively. At 48 hpi, NTHi375 counts were lower in resveratrol treated (square) than in control vehicle administered (circle) zebrafish (p < 0.0001). Perfusion solution-DMSO (1:1) was used as vehicle solution.