Fig. 2.
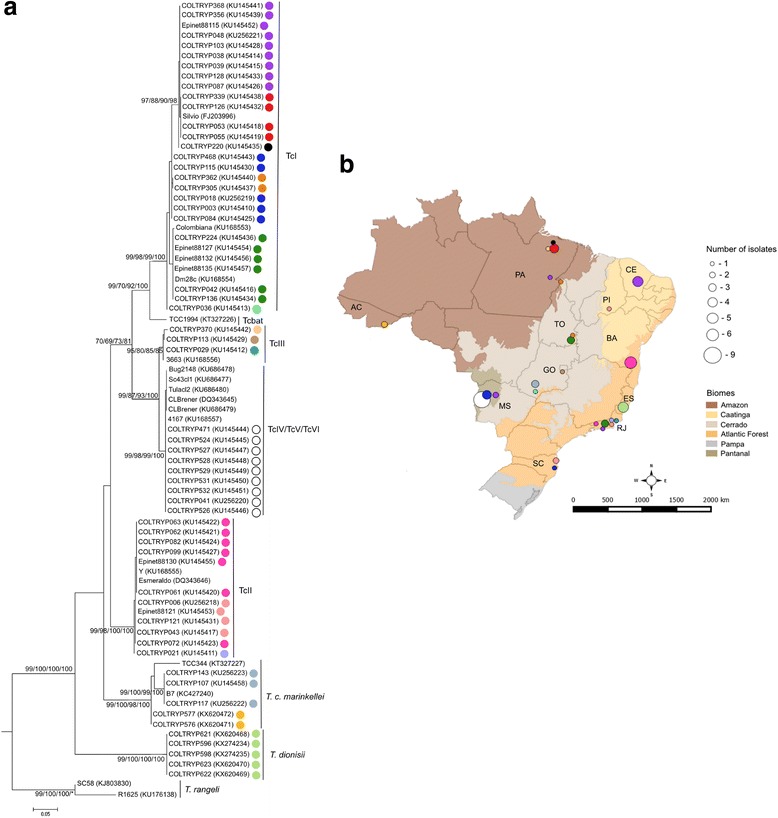
Phylogenetic tree based on cox1 and the geographical origin of the isolates under study. a The cox1 gene differentiates T. cruzi DTUs TcI, TcII, TcIII and TcIV, Tcbat, T. c. marinkellei, T. dionisii and T. rangeli. The heterozygous hybrids TcV and TcVI cannot be differentiated and were placed into the same cluster as TcIV. The numbers at the nodes correspond to NJ, ML, MP and BI support values, respectively (only values >60 are shown). The scale-bar shows the number of nucleotide substitutions per site. The different haplotypes correspond to the diversity observed in cox1 sequences and are represented by colors in the tree. b The map represents the distribution of the characterized isolates among Brazilian biomes. Each colored circle indicates a different haplotype. Circle size represents the number of haplotypes. Abbreviations: Brazilian states: AC, Acre; BA, Bahia; CE, Ceara; ES, Espírito Santo; GO, Goiás; MS, Mato Grosso do Sul; PA, Pará; PI, Piauí; RJ, Rio de Janeiro; SC, Santa Catarina; TO, Tocantins
