Figure 1.
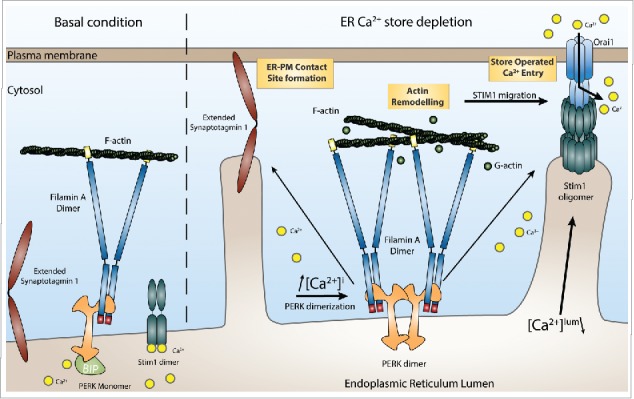
Functional consequences of the interaction between PERK and FLNA on ER-PM contact site formation. Protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK) interacts with Filamin A (FLNA) in resting conditions. After endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-Ca2+ store depletion and subsequent cytosolic Ca2+ elevation, the cytosolic domain of PERK dimerizes. This dimerization event strengthens the interaction of PERK with FLNA. This leads to actin rearrangement and altered actin polymerization dynamics, allowing efficient Stromal interaction molecule 1 (STIM1) and Extended Synaptotagmin-1 (E-Syt1) translocation to the plasma membrane (PM) and the formation of ER-PM contacts.
