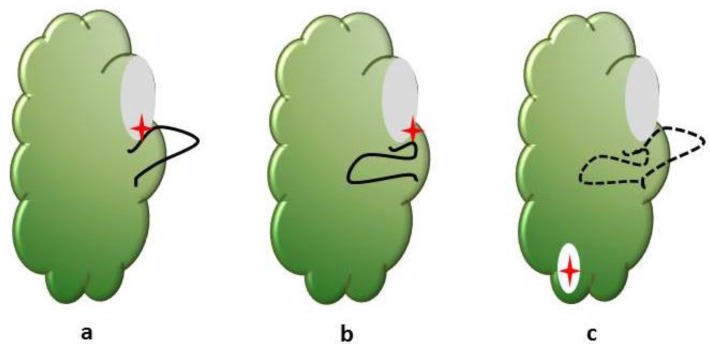
Figure 1.
The activation loop of the protein kinase domain regulates access to the ATP binding site. The conformation of a conserved Asp-Phe-Gly (DFG) motif within the activation loop is used to categorize the binding mode of inhibitors. The common types of kinase—kinase inhibitor interactions include: (a) Type I inhibitors (red star) bind the ATP binding site (grey) of the protein kinase domain (green). The aspartate side chain in the conserved DFG motif at the beginning of the activation loop (black) faces into the active site; (b) Type II inhibitors bind a flipped conformation of the DFG motif in which the aspartate side chain faces outwards; (c) Allosteric ligands bind to binding pockets (white) that do not overlap with the active site of the kinase. The DFG motif conformation is not important. These binding pockets can be adjacent to the active site or distant from the active site.