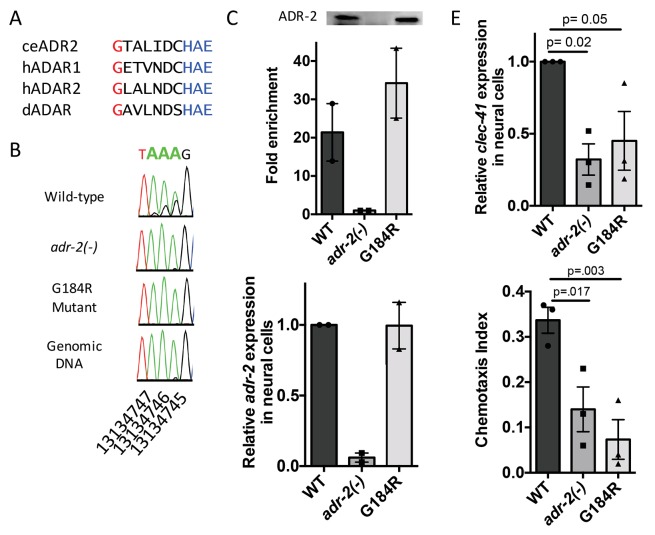
Figure 6. Deamination is required for both proper clec-41 expression and proper chemotaxis.
(A) Alignment of ADAR sequences from several species demonstrating conservation of the Glycine residue at position 184 in the C. elegans ADR-2 protein. This G is near the conserved HAE deamination motif and is mutated to arginine (R) in the adr-2(G184R) worms. (B) RNA from adr-2(G184R) worms was isolated and compared to RNA from wild-type and adr-2(-) worms. RT-PCR and Sanger sequencing of the clec-41 3’ UTR was performed for all three strains. The chromosomal coordinates (ce11) for each editing site are listed below each chromatogram. The nucleotides at each position are represented with a different color (Green = Adenosine, Black = Guanosine, Blue = Cytidine, Red = Thymidine). A-to-I editing sites can be identified by peaks that are green (A) in the amplified genomic DNA and black (G) or a mixture of black (G) and green (A) in the cDNA. (C) Lysates from WT, adr-2(-) and adr-2(G184R) worms were subjected to an ADR-2 immunoprecipitation (IP). Western blotting of the IP samples with an ADR-2 antibody indicate similar levels of ADR-2 in the WT and adr-2(G184R) IPs. qRT-PCR was performed on both RNA from the input lysates as well as the IP samples. The levels of clec-41 in the IP samples was divided by the level of clec-41 in the lysate and the fold enrichment of this ratio for WT and adr-2(G184R) normalized to the negative control adr-2(-) was determined. (D–E) RNA was isolated from neural cells from wild-type (WT), adr-2(-) and adr-2(G184R) worms. qRT-PCR analysis of (D) adr-2 and (E) clec-41 expression was analyzed in neural cells of all three strains. The endogenous control gpd-3 was used to normalize expression levels. (F) Chemotaxis Index of WT, adr-2(-) as well as adr-2(G184R) worms to trimethylthiazole (1:10,000 dilution) was determined from 3 independent biological replicates. One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s Multiple Comparisons Correction.
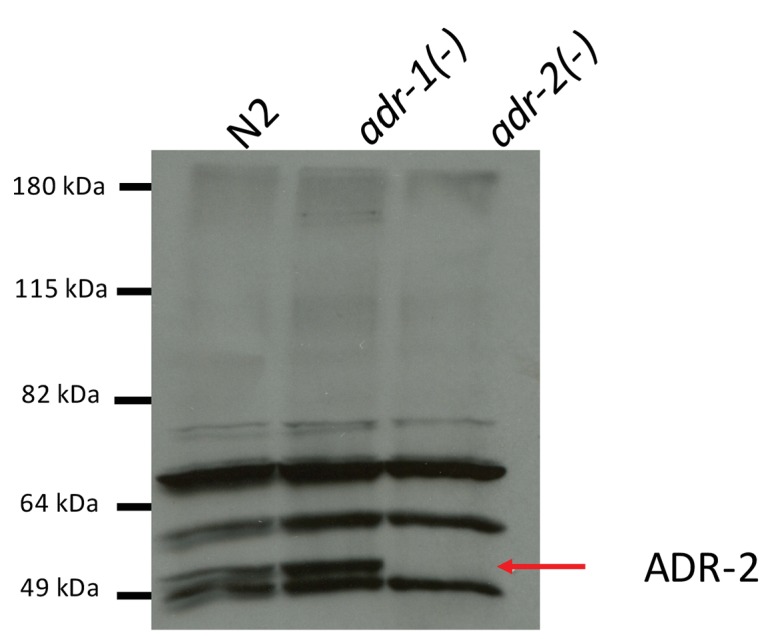
Figure 6—figure supplement 1. Specificity of ADR-2 Antibody.