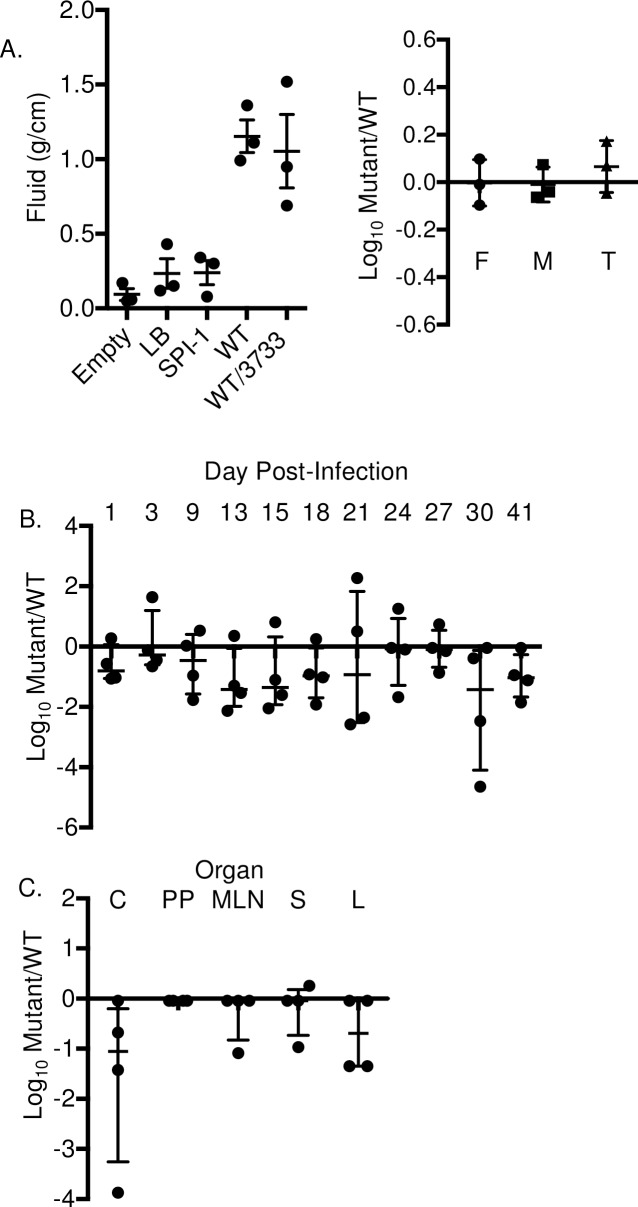
Fig 5. ΔpyrE mutant is able to colonize and persist in mice and calves in the levels similar to wild type.
(A) Bovine ligated ileal loops were infected with 1x109 CFU of a 1:1 mixture of the ΔpyrE mutant and wild type, HA877 (HA420 ΔphoN::NalR pWSK29) by intraluminal injection. After 12 hours post-infection loops were excised and the amount of luminal fluid was determined as a gross measure of inflammation. Luminal fluid (F), mucus (M) and tissue (T) were collected and processed for CFU determination. Infection was performed in 3 different animals. (B) Four CBA/J mice were infected with 1x109 CFU of a 1:1 mixture of the ΔpyrE mutant and wild type, HA431 (HA420 ΔphoN::KanR) by gavage.) Feces were collected every three days, and the CFU of each strain was determined by serial dilution and plating. (C) At 41 days post-infection, the cecum (CC), Peyer’s patches (PP), mesenteric lymph nodes (MLN), spleen (S), and liver (L) were excised, and processed as described in Fig 1. Data is shown as the ratio of mutant to wild type recovered, normalized to the input ratio, and converted to logarithmically. The median is indicated. Statistical significance was determined by using a Student’s two-tail t-test with p < 0.05.