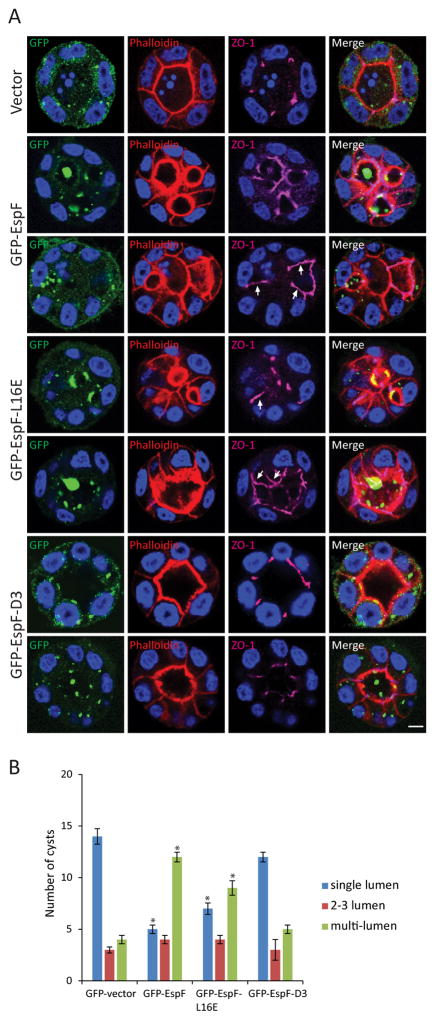
Figure 7.
EspF prevents cyst formation. MDCKII cells were transfected with GFP-vector, GFP-EspF, GFP-EspF-L16E or GFP-EspF-D3, and after 24h placed as a single-cell suspension in Matrigel; cyst formation occurred after 2–3 days. Cysts were fixed and phalloidin (red) and ZO-1 (magenta) were used to label the lumen and the TJ region, respectively. Visualization of GFP was used to determine cysts containing transfected cells. A) Representative confocal images of cysts. EspF and EspF-L16E displaced ZO-1 from tight junctions to the lateral membrane (A, arrows). In contrast, cyst morphogenesis and ZO-1 localization in the presence of GFP-EspF-D3 expression was not different from that seen with GFP-vector. Scale bar, 10 μm. B) Twenty cysts from each group harboring transfected cells were analyzed for the number of lumens formed: single-lumen, 2–3 lumens and multi-lumen. Expression of GFP-EspF and EspF-L16E increased the number of multi-lumen (>3) cysts compared to GFP-vector. Data represent the mean ± SEM (n=3); *P < 0.05 values were calculated using Student t-test analysis.