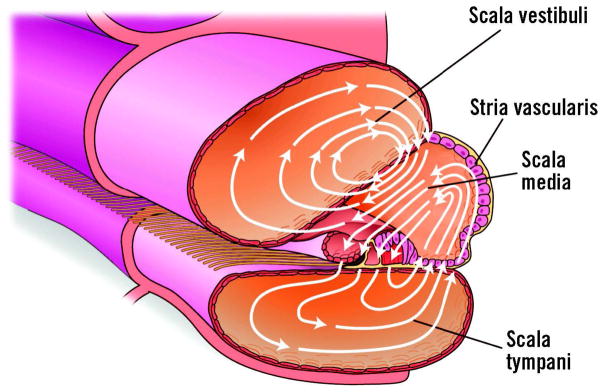
Figure 7.
Cross section of the cochlea showing the flow of ions making up the silent current. There are three fluid-filled chambers. The scala vestibuli and scala tympani contain a conventional extracellular fluid called perilymph, whereas the scala media contains endolymph that is high in potassium and low in sodium. The stria vascularis maintains an endolymphatic potential and electrochemical gradient that drives the silent current (arrows). The metabolically active stria vascularis pumps potassium into the middle cochlear compartment. The potassium passes through the hair cells into the scala tympani and then back to the stria vascularis. There is also a passive route for potassium through the cells, forming the boundary between the scala media and scala vestibuli before returning to the stria vascularis through the perilymph. The silent current is the power source for OHC electromotility.