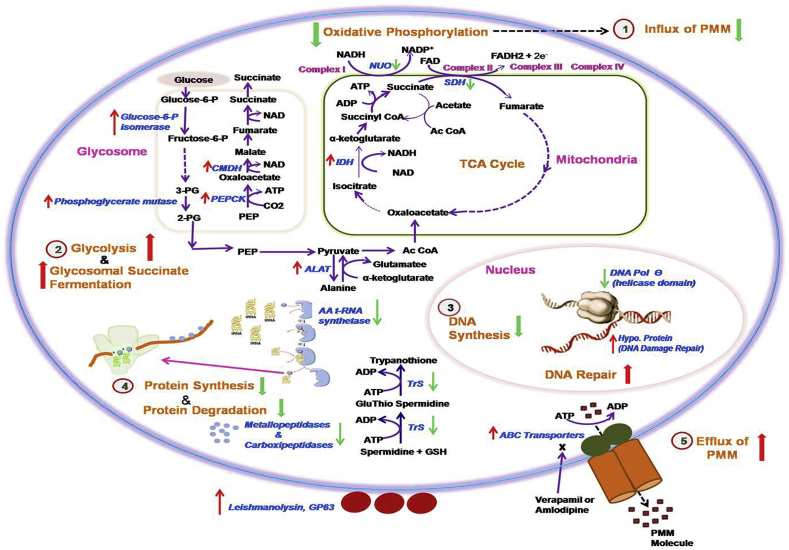
Fig. 4.
Predicted adaptations in L.donovani in PMM resistance. Genes altered in PMM-R parasites are represented here. Genes marked with up and down arrow represent respectively the up-regulated genes and the down-regulated genes in PMM-R parasites. 1,2,3,4 and 5 are probable adaptations in PMM-R parasites.1. Down-regulation of oxidative phosphorylation leads to reduced influx of PMM drug, 2. Enzyme for glycolysis and glycosomal succinate fermentation were up-regulated indicating increased substrate level phosphorylation, 3. Down-regulated DNA polymerase θ suggesting reduced DNA synthesis. Hypo. protein responsible for DNA damage repair were up-regulated 4.Tryptophenyl-t-RNA synthatase and several ribosomal proteins were down-regulated suggesting reduced protein synthesis, Down-regulation of metallo-and carboxipeptidases indicated reduced protein degradation, 5. Up-regulation of ABC transporters and reversion of resistant phenotype in presence of modulators, verapamil or amlodipine suggested probable role of ABC transporters in selection of PMM resistance. Abbreviations used are as follows: 2-PG, 2-phosphoglycerate; 3-PG, 3-phosphoglycerate; AA t-RNA Synthetase, Aminoacyl t-RNA Synthetase; Ac CoA, Acetyl Coenzyme A; ALAT, Alanine aminotransferase; CMDH, Cytosolic malate dehydrogenase; DNA pol. θ, DNA Polymerase θ; Fructose-6-P, Fructose-6-phospahet; Glucose-6-P, Glucose-6-phosphate; GSH, Glutathione; Hypo. Protein, Hypothetical protein; IDH, Isocitrate dehydrogenase; NUO, NADH ubiquinone oxidoreductase; PEP, Phosphoenol pyruvate; PEPCK, Phosphoenol pyruvate carboxykinase; SDH, Succinate dehydrogenase; TrS, Trypanothione synthetase.