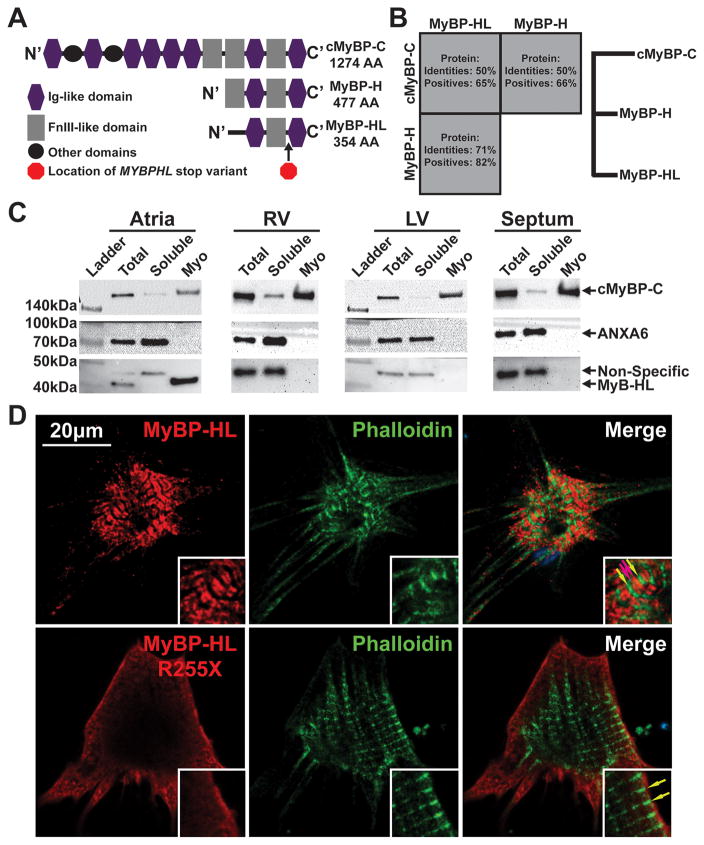
Figure 4. MYBPHL is structurally similar to other myosin binding proteins and interacts with the myofilament.
A. Diagram of the Immunoglobulin (Ig)-like and fibronectin type 3 (FnIII)-like domains that comprise cMyBP-C, MyBP-H, and MyBP-HL; the location of the premature stop in MyBP-HL created by the identified variant is marked between the C’ Ig and FnIII domains. B. Protein sequence conservation and phylogeny between the myosin binding protein family members show that MyBP-H and MyBP-HL are more closely related to each other than to cMyBP-C. C. Immunoblot analysis of total tissue homogenate, soluble protein, and myofilament fractions from atria, right and left ventricle, and ventricular septum detect MyBP-HL in the atrial myofilament, with cMyBP-C and annexin-6 used as myofilament and soluble controls, respectively. D. Immunofluorescence microscopy of neonatal mouse cardiomyocytes transfected with N’-terminally Myc-tagged full-length and R255X MyBP-HL constructs showed myofilament patterned MyBP-HL localization that is not observed with the R255X variant (green and red arrows, insets).