Fig. 4.
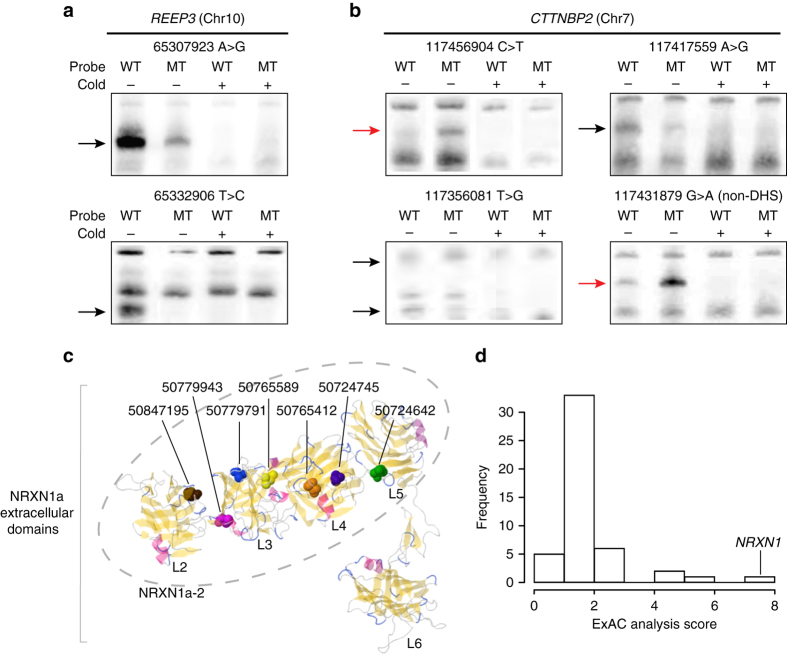
Top genes validate in functional assays in context of known protein structure and in comparison to ExAC. EMSA of all 17 candidate regulatory variants in a REEP3 and b CTTNBP2 reveals that six variants either decrease (black arrows) or increase (red) protein binding when the variant sequence (MT) is compared with the reference allele (WT). The signal disappears when competing unlabeled probes (Cold+) are added, confirming the specificity of the DNA-protein binding. Raw images as well as EMSA results for experimental replicates and for other candidate regulatory variants that showed weak-binding changes are shown in Supplementary Fig. 8. c All seven of the candidate missense variants in NRXN1, shown here as colored elements, alter the extracellular postsynaptic-binding region of our top-scoring protein isoform NRXN1a-2 43, 59, 60. Of the six extracellular LNS (laminin, nectin, sex-hormone-binding globulin) domains in the longer isoform NRXN1a, five with known protein structure are shown and labeled L2-L6. NRXN1a-2 includes four of these domains (L2–L5; dashed ellipse). d The isoform-based test comparing OCD cases to ExAC finds NRXN1 as the top-scoring gene with genome-wide significance. The ExAC analysis score is defined as the ratio of χ 2 statistics (, where n = total number of isoforms, Oi = number of non-reference alleles observed in isoform i, Ei = number of non-reference alleles expected from ExAC in isoform i) between OCD vs. ExAC comparison and control vs. ExAC comparison