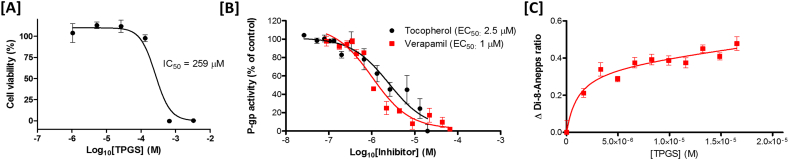
Fig. 1.
The P-gp inhibition activity of TPGS in a neuronal cell line closely matches its dipole potential modulating effects [A] Dose response curve (AlamarBlue) for a retinal neuronal cell line after 18 h incubation with TPGS (n = 3). [B] Comparison of the effect of TPGS and verapamil hydrochloride on P-gp activity in the same retinal neuronal cell line. Data expressed as the mean ± SE (n = 6). The figure shows a dose-dependent decrease in P-gp activity with both verapamil hydrochloride and TPGS fit four parameter dose-response curves. [C] Change in membrane dipole potential on titration of TPGS into retinal neuronal cell line as determined by di-8-ANEPPs fit best to a hyperbolic binding equation with a dissociation constant similar to the IC50 of TPGS for P-gp (2.48 ± 0.06 μM versus 2.22 ± 0.03 μM respectively). Results are means ± SE.