Figure 1.
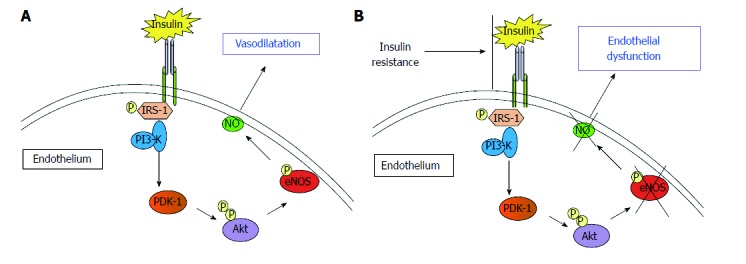
The binding of insulin to its receptor activates a series of phosphorylations of downstream receptors that finally activate nitric oxide-production by endothelial nitric oxide synthase. A: The release of nitric oxide (NO) causes endothelium dependent vasodilation; B: Insulin-resistance causes the reduction of Insulin-induced activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS). This is associated with reduction of NO bioavailability and, finally, endothelial dysfunction.
