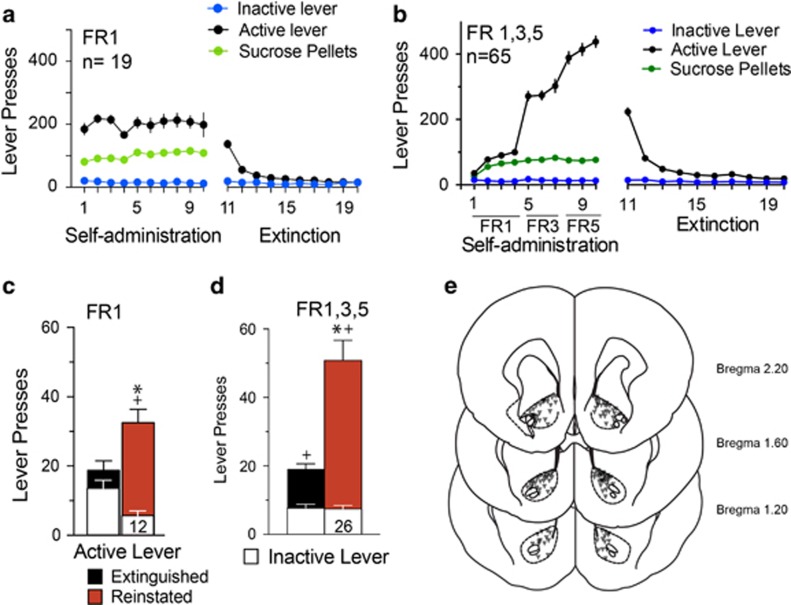
Figure 1.
Rat sucrose self-administration, extinction training, and cue-induced reinstatement. (a) Sucrose self-administration with fixed ratio 1 (FR1) and extinction training, n=19. (b) Sucrose self-administration with increasing schedule of reinforcement FR1/FR3/FR5 and extinction training, n=65. (c) Cued-reinstatement after an FR1 schedule and extinction training corresponding to the n=12 vehicle microinjections. Two-way ANOVA active/inactive lever F(1,22)=25.21, p<0.001, extinction/reinstatement F(1,22)=1.73, p=0.202, interaction (F(1,22)=22.62, p<0.001). (d) Cued-reinstatement after an FR1/FR3/FR5 schedule sucrose self-administration and extinction training corresponding to n=26 vehicle microinjections. Two-way ANOVA active/inactive lever F(1,25)=65.08, p<0.001, extinction/reinstatement (F(1,25)=32.63, p<0.001, interaction F(1,25)=37.65, p<0.001). *p<0.05 comparing extinction to reinstatement active lever pressing using a Sidak’s multiple comparisons post-hoc test. +p<0.05 comparing active and inactive lever pressing during extinction or reinstatement. (e) Location of injector tips in the NAcore that were used for all microinjection studies. Numbers indicate distance from bregma based on the rats atlas of Paxinos and Franklin (1997). Figure 1a, b and d include all rat behavioral data and histology, Figure 1c and d pool the reinstatement of all the saline-treated animals after FR1 or FR1/FR3/FR5 schedules of reinforcement.