Fig. 7.
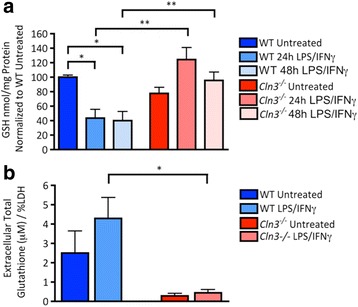
Cln3 −/− astrocytes fail to secrete glutathione. Wild type (WT) and Cln3-deficient (Cln3 −/−) primary cortical astrocytes were analyzed for their ability to synthesize and secrete reduced glutathione (GSH). a Reverse phase HPLC was used to measure the intracellular levels of GSH in WT and Cln3 −/− astrocytes treated with LPS/IFNγ for 24 or 48 h, or from untreated samples. The GSH levels in each sample were normalized to the total amount of protein in that sample and results presented in nmol/mg of protein. Additionally, these results were normalized to untreated WT astrocyte GSH levels in each experiment. LPS/IFNγ stimulation caused a significant decrease in the intracellular levels of GSH in WT astrocytes but not in Cln3 −/− astrocytes. b The GSH-Glo kit was used to measure the total amount of GSH secreted into the medium over an 8 h period by cultures of untreated and LPS/IFNγ treated WT and Cln3 −/− astrocytes. TCEP (12uM) was used to convert the oxidised form of glutathione (GSSH) to GSH to measure the total amount of GSH in each sample. These results were normalized to released %LDH from total LDH. LPS/IFNγ treated Cln3 −/− astrocytes secreted significantly reduced levels of GSH compared to LPS/IFNγ treated WT astrocytes
