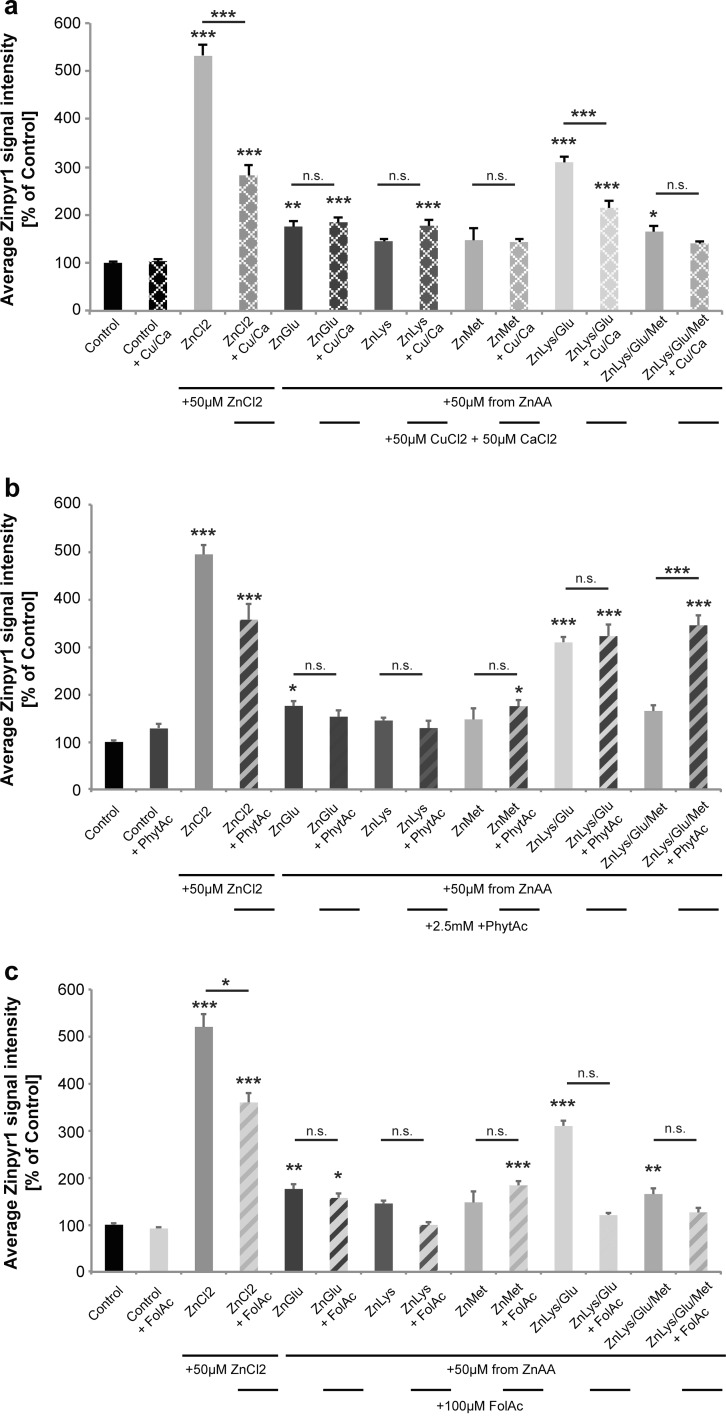
Fig. 2.
Effect of antagonistic factors on uptake of Zn from ZnAAs in Caco-2 cells. Zinpyr-1 fluorescence intensity of Caco-2 cells. a Application of Zn uptake antagonists calcium (provided as CaCl2) and copper (provided as CuCl2) together with ZnCl2 solution and ZnAAs. A significant inhibitory effect on Zn uptake from ZnCl2 solution is seen. No significant inhibition of the uptake of Zn delivered by ZnGlu, ZnLys, ZnMet, and ZnLys/Glu/Met was observed. The uptake of ZnLys/Glu was significantly inhibited. b Co-application of Zn uptake antagonist phytic acid (PhytAc). Co-application of ZnCl2 and phytic acid leads to significantly less increase in intracellular Zn levels compared to cell treated only with ZnCl2 solution. No significant antagonistic effect was observed upon co-application of phytic acid and ZnGlu, ZnLys, ZnMet, ZnLys/Glu, and ZnLys/Glu/Met. Uptake of ZnLys/Glu/Met was higher in presence of phytic acid. Phytic acid was used in a molar ratio Zn:PhytAc = 1:50 (n = 10). c Co-application of Folic acid (FolAc). Significantly less Zn uptake via ZnCl2 solution (FolAc was used with 100 μM concentration) is observed. A significant inhibitory effect on the uptake of ZnLys, ZnLys/Glu, and ZnLys/Glu/Met was observed. Only ZnGlu and ZnMet are unaffected, although ZnMet did not significantly increase intracellular Zn levels within 30 min (n.s. not significant)