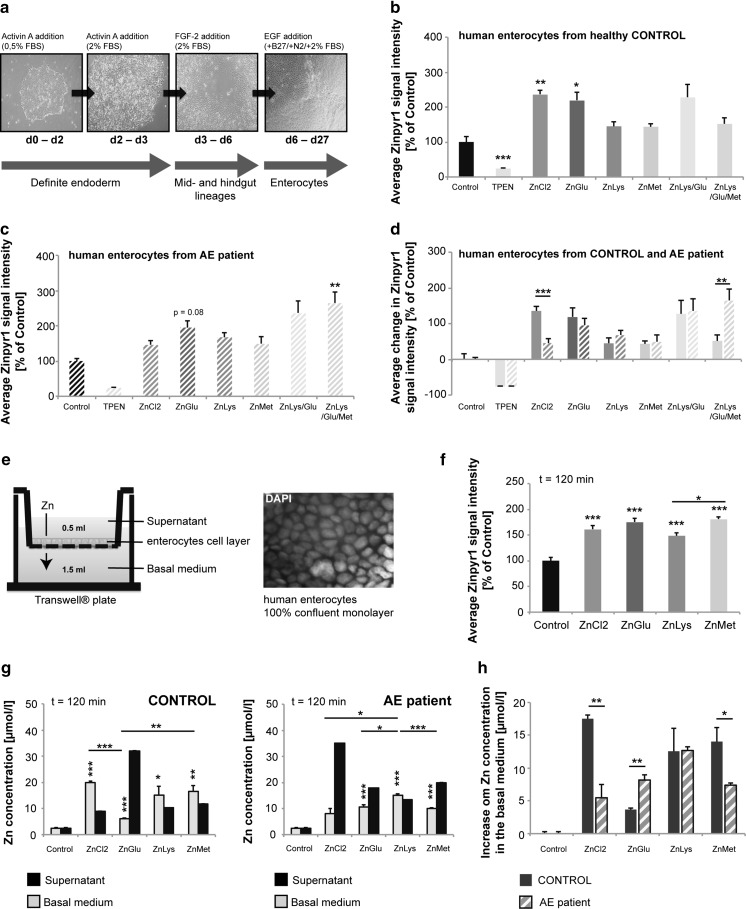
Fig. 3.
Zn uptake in human enterocytes differentiated from healthy controls and patients with Acrodermatitis enteropathica. a Overview of the protocol for generation of enterocytes from hIPSC of a healthy control and AE patient. b, c Enterocytes were exposed to ZnCl2 solution (50 μM) or ZnAAs delivering an equivalent of 50 μM Zn for 30 min. Treatment with the Zn chelator TPEN confirmed the specificity of the Zinpyr-1 signal. b Intracellular Zn levels in enterocytes of the healthy control are significantly increased after treatment with ZnCl2 solution and ZnGlu. ZnLys, ZnMet, ZnLys/Glu and ZnLys/Glu/Met did not significantly increase intracellular Zn within 30 min after application. c Intracellular Zn levels in enterocytes of the AE patient did not show a significant increase after treatment with ZnCl2. Application of ZnLys/Glu/Met (significant) and ZnGlu (as trend) leads to an increase in intracellular Zn levels. d A significant difference in uptake of Zn from ZnCl2 solution between enterocytes from Control and the AE patient was detected. Uptake of ZnAAs is not significantly lower in enterocytes from the AE patient compared to the Control. Uptake from ZnLys/Glu/Met was significantly higher in cells from the AE patient. e Enterocytes differentiated from hIPSC were plated on the filter of a transwell® system. ZnCl2 solution or ZnAAs were applied to the supernatant. After 120 min, the supernatant and the basal medium were removed. Cells on the filter were grown until they were 100% confluent and are visualized by DAPI staining of cell nuclei. f After incubation with ZnCl2 or ZnAAs, a significant increase in Zinpyr-1 staining in cells (n = 10) was detected. g Left: Using cells from the Control, all treatments resulted in a significant increase of Zn concentration in the basal medium (measured by AAS). The absorption of ZnGlu was significantly less compared to ZnCl2 solution and ZnMet. Right: Using cells from the AE patient, incubation with ZnCl2 solution did not result in a significant increase of Zn concentration in the basal medium compared to untreated control cells, while application of all ZnAAs significantly increase the Zn concentration in the basal medium. The absorption of ZnLys was significantly higher compared to ZnCl2 solution, ZnGlu and ZnMet. h Comparing the healthy control and the AE patent, significant differences were detected in the absorption of Zn from ZnCl2 solution and after application of ZnGlu and ZnMet