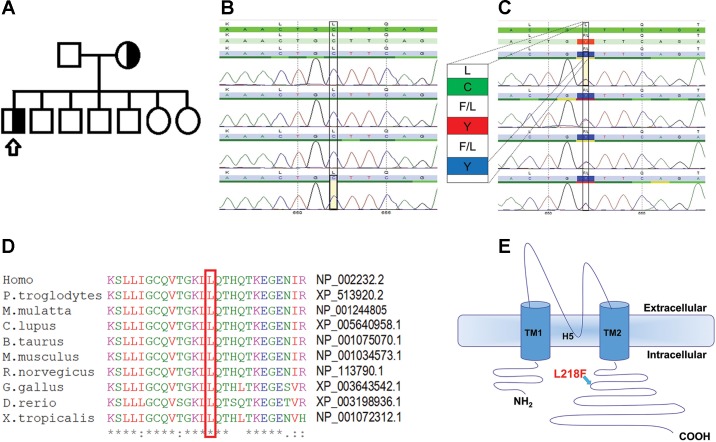
Fig. 1.
Detecting and analyzing the mutation. A: pedigree of the patient’s family indicating heterozygous state for the KCNJ10 mutation in both mother and proband. Squares represent males and circles females; arrow points to our affected proband. Detection of mutation was done by sequencing. B and C: electropherograms of KCNJ10 exons for the WT control (B) and the L218F mutation (C) in our patient. D: protein sequence of KCNJ10 from various species aligned using MUSCLE 3.6. The GenBank accession numbers for KCNJ10 of each species are indicated. E: schematic topology model of the human KCNJ10 subunit according to UniProt (ID P78508; http://www.uniprot.org/). The L218F variant lies in the cytoplasmic COOH-terminal domain.