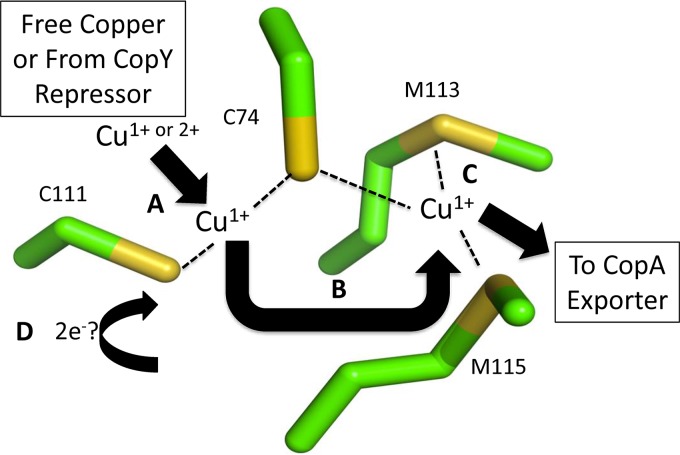
FIG 8 .
Cupredoxin mechanism of CupA. (A) Chelated copper obtained from CopY or other proteins is reduced to Cu1+ by C74 and C111 or oxidizes the donor cysteines. Reducing activity is more efficient with both cysteines present. (B) Cu1+ is transferred from site 1 (C74 and C111) to site 2 (C74, M113, and M115) (C) Site 2 holds Cu1+ until transfer to CopA for efflux can occur. (D) The oxidized cysteine residues are reduced from a currently unknown source, thus resetting CupA to receive, reduce, and chaperone copper to the CopA exporter. Carbon atoms are green, and sulfur atoms are yellow. PDB code 4F2E.