FIG 4 .
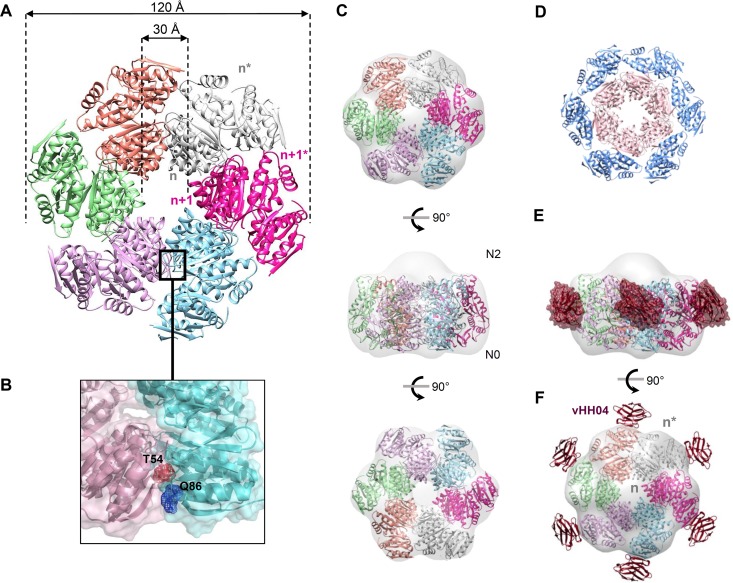
Atomic model of the XcpQN012 dodecameric complex. (A) Model of XcpQN012 dodecamer generated by SymmDock by imposing a C6 symmetry. The six XcpQN012 dimers are shown in cartoon form with a specific color. (B) The residues Thr54 and Gln86 in the N0n+2-N0n+3 interface are shown in stick and mesh presentations. (C) Top, side, and bottom views of the dodecameric XcpQN012 model docked into the EM map of the complex. (D) The dodecameric XcpQN012 model is organized into two peripheral and internal rings. The peripheral ring is colored in blue and presents the denoted subunits of each of the six dimers. The inner ring is colored in pink and presents the un-stranded subunits of each of the six dimers. (E) Model of vHH04-XcpQN012 complex. The crystal structure of the vHH04-XcpQN012 complex is overlaid with the dodecameric model of XcpQN012. Only six vHH04s presented in hot pink are able to bind the XcpQN012 complex. (F) Side view of the 6:12 vHH04-XcpQN012 complex docked into the EM map.