Figure 1.
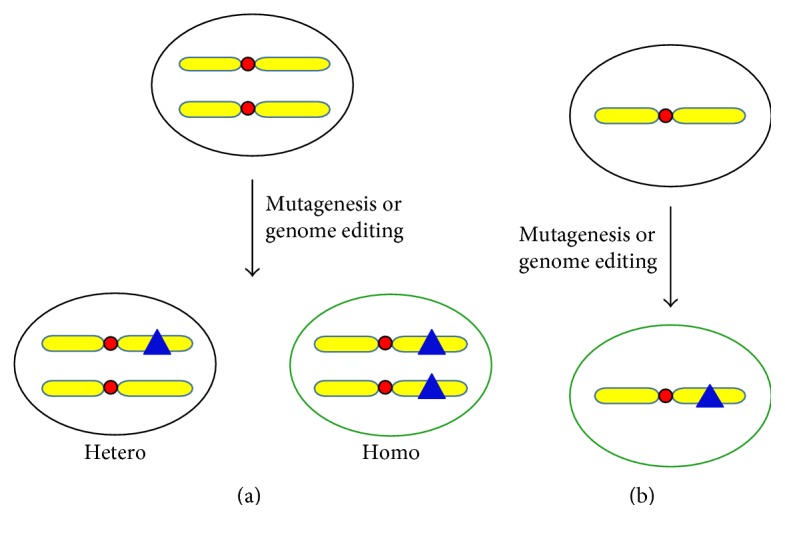
The advantage of haploid cells over diploid cells in genetic screening. (a) When a recessive mutation (shown by a blue triangle) is introduced into a diploid cell either by random mutagenesis or by genome editing, heterozygous or homozygous cells can be derived. However, the phenotype (illustrated by green circles) of the recessive mutation can be only detected in homozygous cells, but not in heterozygous cells. (b) Haploid cells only have one set of chromosomes. Once the recessive mutation is introduced into a haploid cell, the cell will display the corresponding phenotype.
