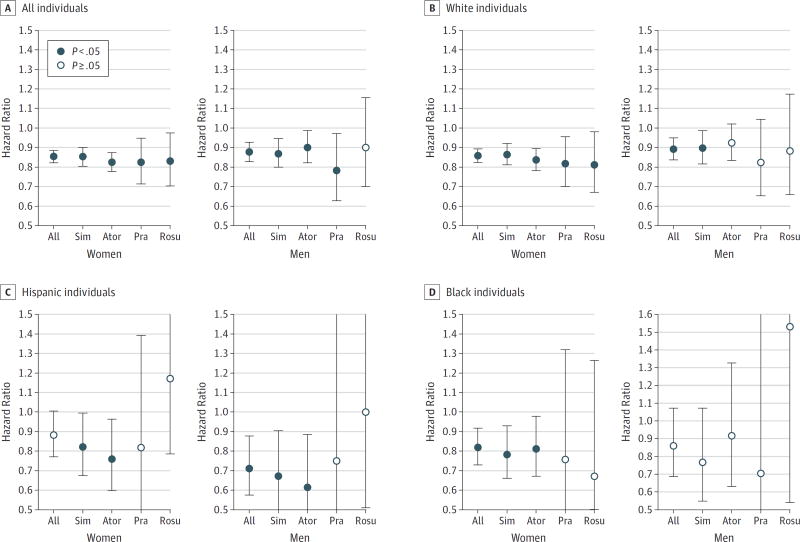
Figure 2. Incidence of Alzheimer Disease Associated With High vs Low Exposure to Statins.
Hazard ratios depicting the relative risk of Alzheimer disease incidence from 2009 to 2013 for those with high vs low exposure to statins. High-exposure individuals are those with days of filled prescriptions in at least the 50th percentile of days in the mean statin-year in at least 2 years of the period from 2006 to 2008. The low-exposure group used the designated statin, but for fewer days, or later in the sample period. Error bars indicate 95%CI (Table 3). Ator indicates atorvastatin; Pra, pravastatin; Rosu, rosuvastatin; and Sim, simvastatin.