Figure 2.
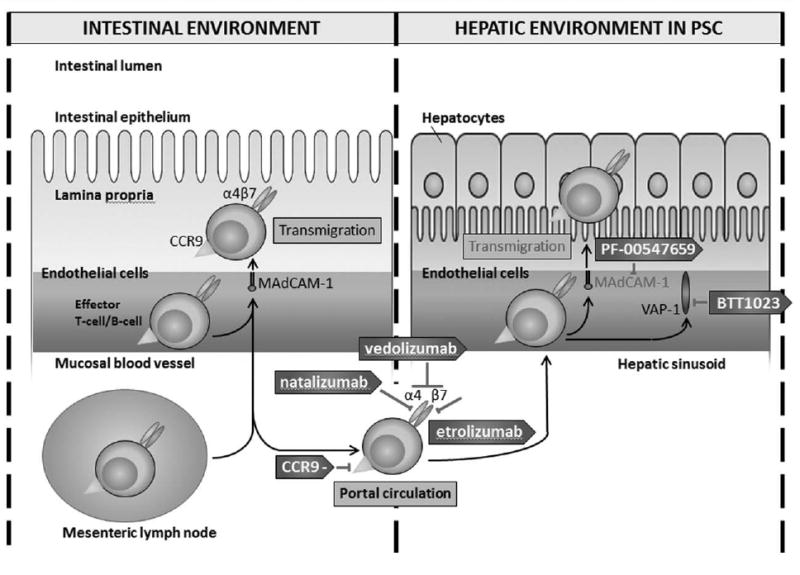
Therapies that are proposed to inhibit the transmigration of gut-derived lymphocytes into the hepatic environment in primary sclerosing cholangitis. In primary sclerosing cholangitis, mucosal vascular address in cell adhesion molecule 1 is aberrantly expressed. This allows aberrant binding and transmigration of gut-derived lymphocytes via α4β7 integrin. Binding and transmigration is further enhanced by vascular adhesion protein-1, which is constitutively present on hepatic endothelial cells and allows lymphocyte recruitment. CCR9–, chemokine receptor 9 inhibitor; MAdCAM-1, mucosal vascular addressin cell adhesion molecule 1; PSC, primary sclerosing cholangitis; VAP-1, vascular adhesion protein-1.
