Fig. 1. Model for the proposed mechanisms of intercellular miRNA cell-to-cell transfer.
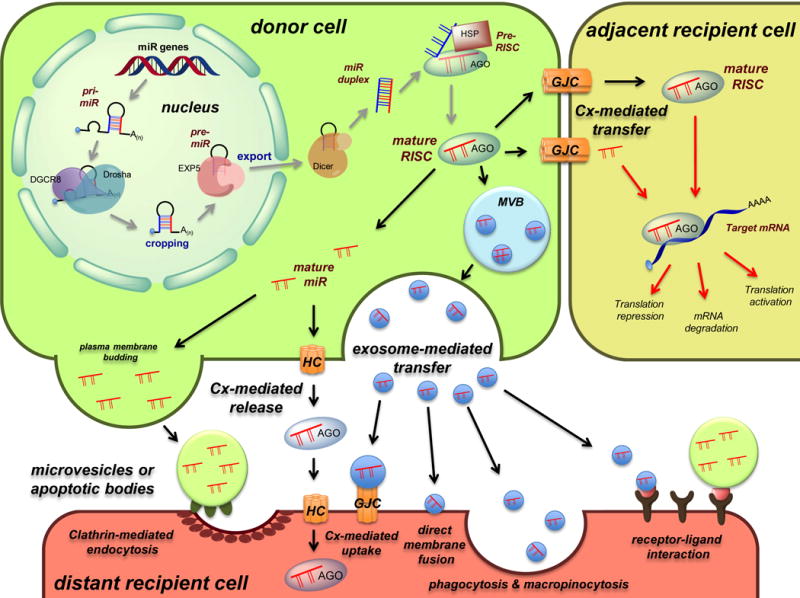
Schematic representation of miR biogenesis (grey arrows), see text for more details. Upon completion of the biogenesis process, the mature RISC complex can regulate mRNA gene expression in the donor cell or can be transferred to adjacent or distant recipient cells to modulate mRNA expression by different manners (red arrows). Cell-to-cell transfer mechanisms include connexin-mediated transfer (via direct gap junctions or through hemichannels) and exosome-mediated transfer (via direct membrane fusion, clathrin-mediated endocytosis, phagocytosis and micropinocytosis, receptor-ligand interaction, or connexin-mediated uptake). HC: hemichannel, GJC: gap junction channel, MVB: multivesicular body.
