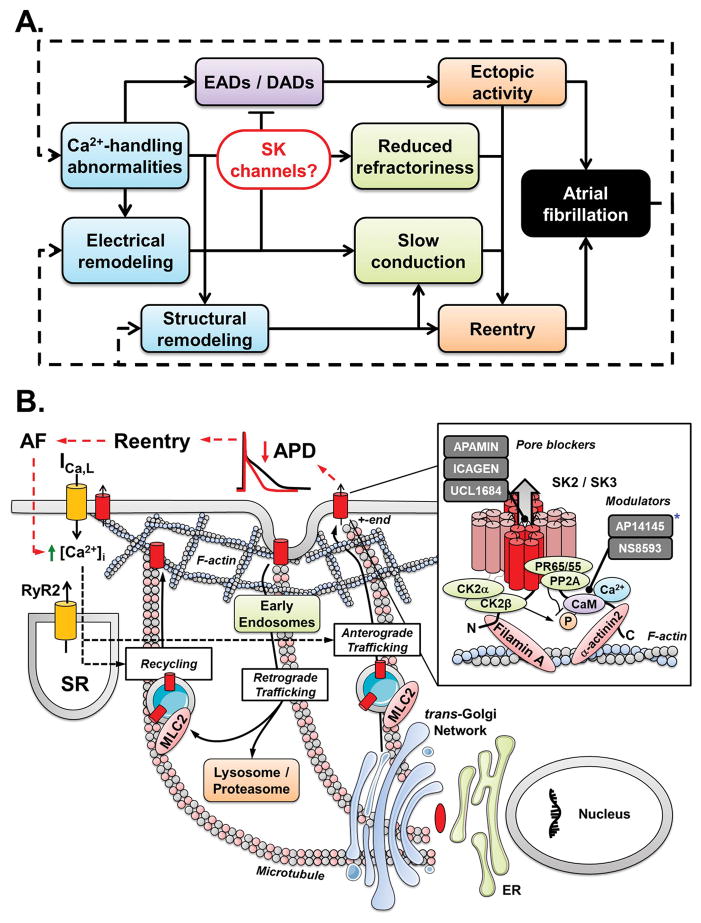
Figure 1.
A. Fundamental mechanisms of atrial fibrillation (AF) and the central role for small-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ (SK) channels linking Ca2+-handling abnormalities and repolarization disturbances. B. Complexity of atrial cardiomyocyte SK-channel regulation involving Ca2+-dependent trafficking and phosphorylation-modulated Ca2+-dependent gating of SK-channels within the macromolecular multiprotein complex.20 The trafficking (anterograde and retrograde) of SK-channels is dynamic and depends on interactions with microtubule and F-actin cytoskeletal proteins. SK2-channels recycle quickly between the plasma membrane and early (recycling) endosomes via a mechanism involving α-actinin2 and filamin A. Myosin light chain 2 (MLC2) is also required for membrane trafficking and localization of SK2-channels. SK-channels are degraded via the lysosome/proteasome system. The precise trafficking pathways of SK-channels in the human atrium need further determination. The Ca2+-dependent gating of SK-channels is mediated by calmodulin (CaM). SK2- and SK3-channels are organized in macromolecular multiprotein complexes including CaM, protein kinases (e.g., casein kinase 2α and 2β; CK2α and CK2β, respectively) and phosphatases (e.g., type 2a; PP2A). CK2 and PP2A alter the Ca2+ sensitivity of SK-channels by phosphorylation (which decreases Ca2+-sensitivity and reduces ISK) and dephosphorylation (opposite effects) of SK-associated CaM at threonine-80. Whether Ca2+-dependent gating of atrial SK channels is similarly regulated by dynamic CaM-mediated phosphorylation in vivo is not established. Grey squares in inset show available SK-channel blockers grouped by their mechanism of action (pore block vs. modulation of Ca2+-dependent gating). * The compound AP14145 presented in the study by Diness et al.13 in the present issue of the journal is listed as modulator based on its structural similarity to NS8593. DADs, delayed afterdepolarisations; RyR2, ryanodine-receptor channels type-2; ICa,L, L-type Ca2+-current; APD, action potential duration; SR, sarcoplasmic reticulum; PR65/55, regulatory PP2A subunit.