Fig. 3.
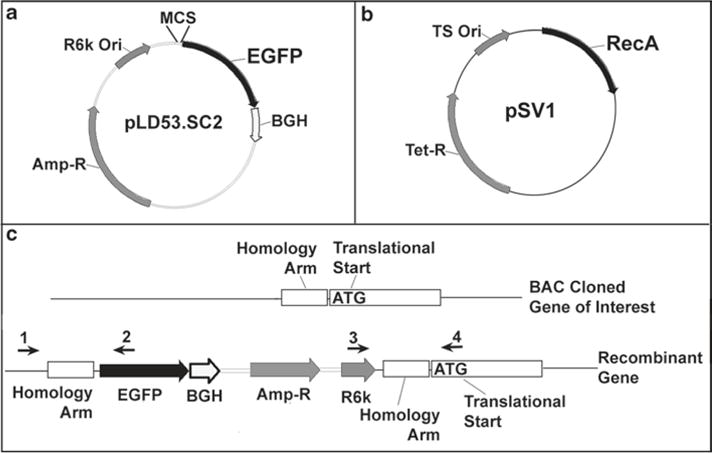
The two vector recombination system using RecA. (a) The pLD53.SC2 vector contains an EGFP reporter gene downstream of a multiple cloning site (MCS), ampicillin resistance, and an R6kγ replication origin. (b) The pSV1 vector contains a RecA recombinase, tetracycline resistance, and a temperature-sensitive replication origin (replicates at 30°C, does not replicate at 42°C). pSV1 is transformed into the bacteria containing the BAC clone of interest to introduce RecA. (c) A homology arm, typically located a few nucleotides upstream of the translational start site, is cloned into the MCS of pLD53.SC2. Recombination is carried out by transforming pLD53.SC2 (with homology arm) into the bacteria containing your BAC clone and pSV1. Recombinants are initially selected for by colony PCR using primers ((1&2) or (3&4)) that flank the homology arm. Final recombinants are verified by diagnostic restriction enzyme digestion and FIGE (see Fig. 4).
