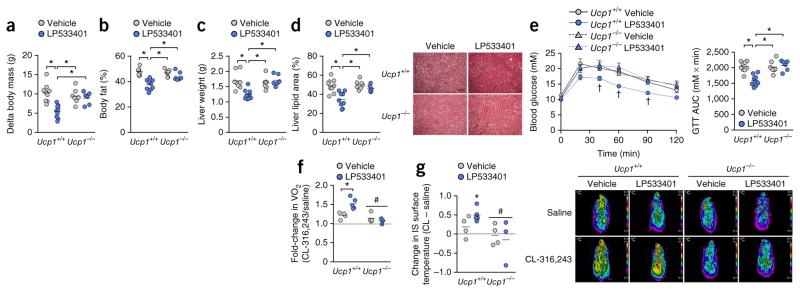
Figure 4.
UCP1 expression is required for the metabolic benefits of Tph1 inhibition. (a,b) Change in body mass after 6 weeks of HFD (a) and adiposity (b) from vehicle- and LP533401- treated Ucp1+/+ and Ucp1−/− mice. (c,d) Liver mass (c) and lipid content (d; right, representative H&E cross-sections) in vehicle- and LP533401- treated mice. Scale bar is 100 μm. (e) GTT and AUC of vehicle- and LP533401-treated Ucp1+/+ and Ucp1−/− mice. For a–e, n = 9 for Ucp1+/+ vehicle and LP533401, n = 7 for Ucp1−/− vehicle and n = 6 for Ucp1−/− LP533401. (f,g) Change in oxygen uptake (f) and dorsal interscapular surface temperature (g) in vehicle- and LP533401-treated mice acutely injected with saline or CL-316,243 (n = 4 for Ucp1+/+ and Ucp1−/− vehicle, n = 5 for Ucp1+/+ LP533401 and n = 3 for Ucp1−/− LP533401). Right (g), representative thermal images of all mice in a given group. Data are expressed as means ± s.e.m. *P < 0.05 relative to indicated groups or versus saline condition. #P < 0.05 relative to wild-type and †P < 0.05 relative to all other groups as determined by two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test.