Figure 1.
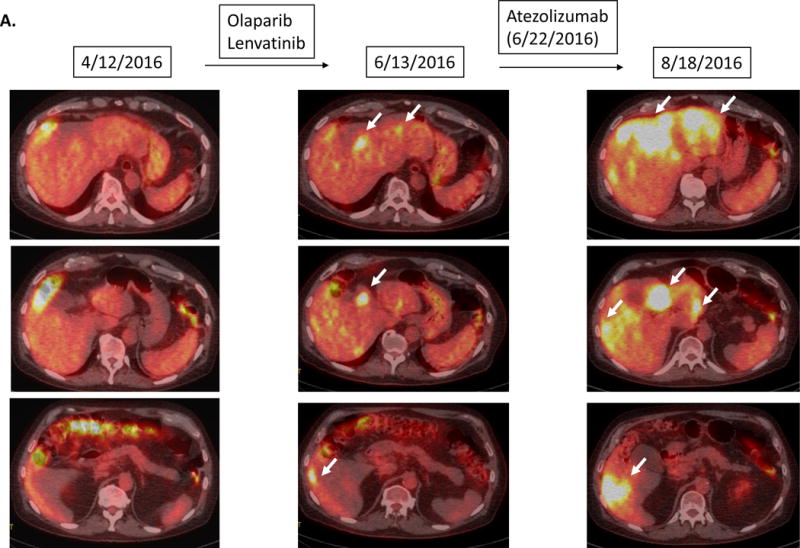
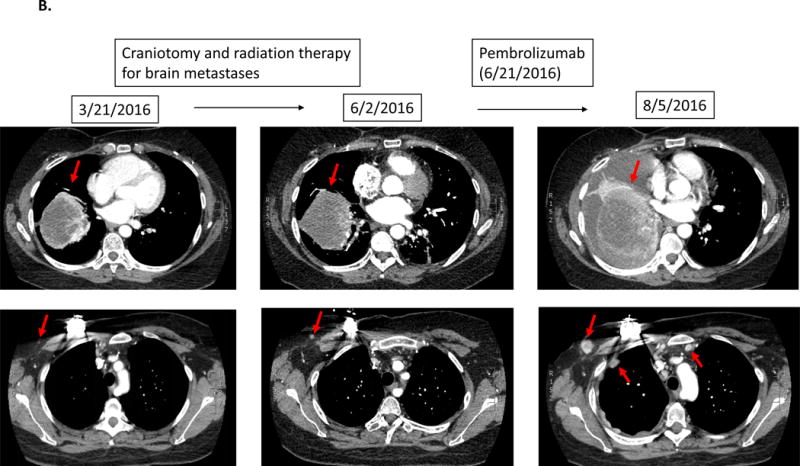
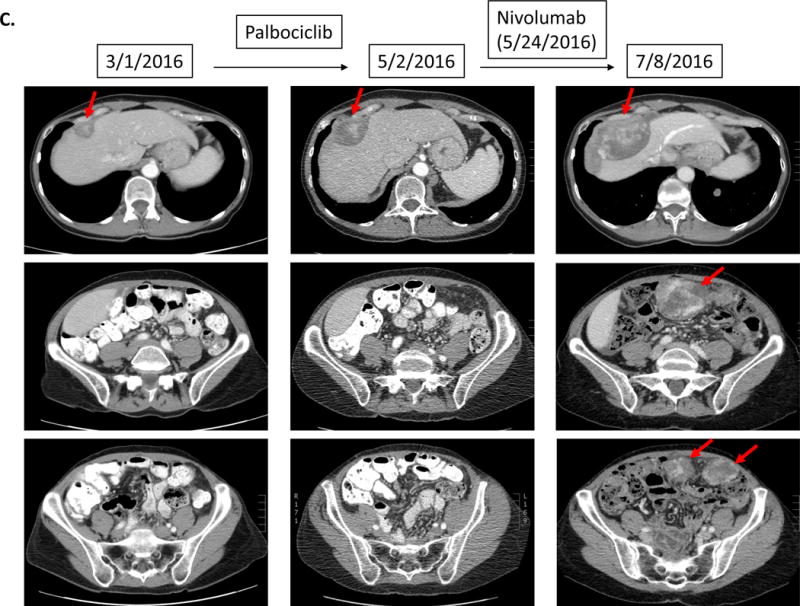
Serial imaging before and after immunotherapy among patients with MDM2/4 amplifications (N=6). Baseline imaging refers to images about 2 months before immunotherapy. Pre-immunotherapy imaging refers to imaging immediately before immunotherapy.
A.
Case #1:
Patient with bladder carcinoma. Tumor showed gradual progression over several months prior to atezolizumab. Restaging 1.9 months after atezolizumab showed a 258% increase in tumor size compared to pre-immunotherapy accompanied by a dramatic increase in PET FDG avidity and new liver masses. Follow up imaging 2.8 months after the initiation of atezolizumab confirmed the progression (imaging not shown) and the patient died soon afterwards.
B.
Case #2:
Patient with triple-negative breast cancer. While receiving local therapy against brain metastases, left lung metastasis was overall stable. However 1.5 months after the initiation of pembrolizumab, a CT scan revealed a 55% increase of the left lung mass as well as new chest wall masses and lymphadenopathy.
C.
Case #3:
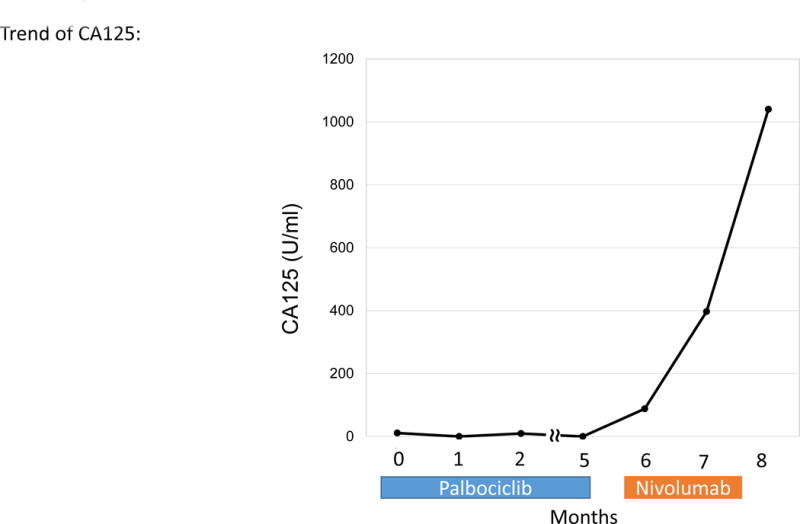
Patient with endometrial stromal sarcoma. Patient had shown increase in tumor size and CA125 (11 to 33 U/mL) over six months. On 1.5 months of nivolumab, CT imaging demonstrated rapid progression of liver metastases and new bulky abdominal masses (overall 242% increase from pre-immunotherapy imaging) (upper panel). CA125 also increased from 33 to 1040 (U/mL) (lower panel).
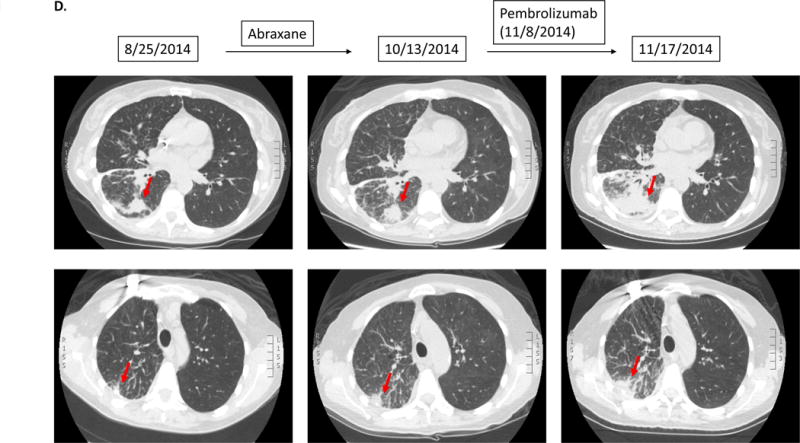
D.
Case #4:
Patient with adenocarcinoma of lung. Patient had gradual progression on Abraxane. Soon after starting pembrolizumab, patient noted severe fatigue/malaise, which prompted the physician to obtain repeat CT imaging. The scan showed rapid progression of known lung metastases (135% increase from pre-immunotherapy).
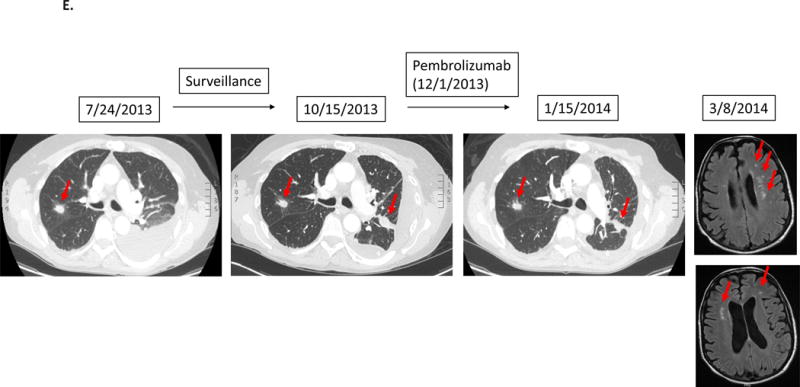
E.
Case #5:
Patient with adenocarcinoma of lung. After first-line chemotherapy, imaging detected new lung disease. Patient was then started on pembrolizumab. However, patient noticed rapidly worsening shortness of breath and severe generalized fatigue. Although CT of the chest showed stable disease, patient was taken off therapy for clinical progression about 1.5 months after the initiation of pembrolizumab. Subsequent MRI of the brain showed multiple new brain metastases.
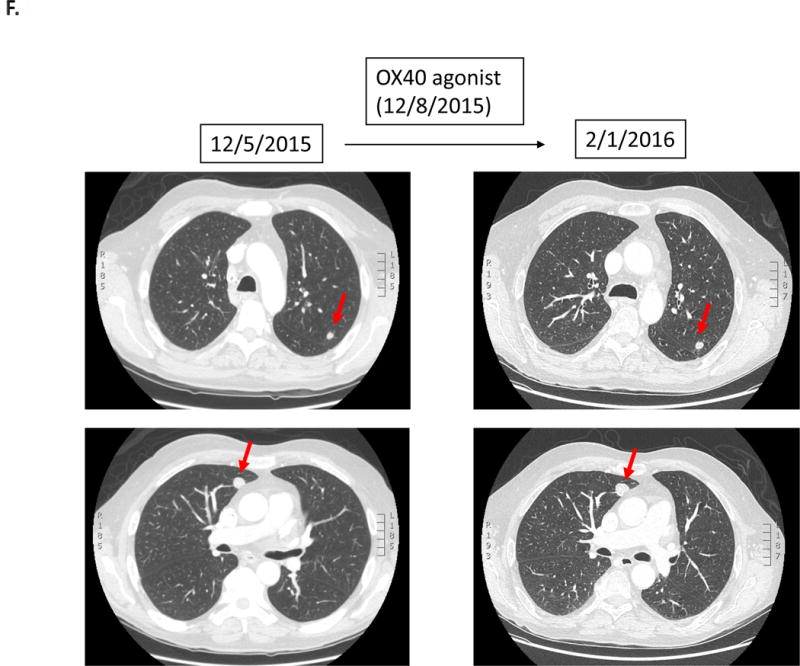
F.
Case #6:
Patient with squamous cell carcinoma of the hypopharynx was treated with an OX40 agonist (third-line therapy). Within 1.4 months, patient was taken off study due to progressive altered mental status secondary to worsening hyponatremia attributed to tumor-associated SIADH. Imaging at the time was stable. The patient died three months later.
