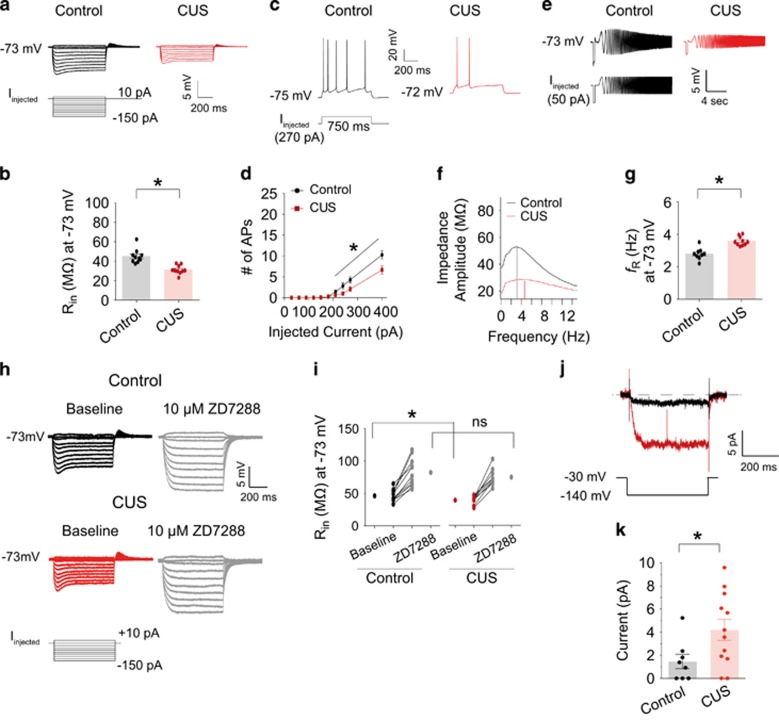
Figure 2.
Upregulation of Ih-related electrophysiological measurements in dorsal CA1 neurons following CUS (a) Representative voltage responses with step current injections at a common membrane potential (−73 mV; 750 ms). (b) Input resistance (Rin) at -73 mV was significantly reduced in dorsal CA1 neurons following CUS. (c) Representative voltage responses with depolarizing current step (270 pA; 750 ms) at resting membrane potential. (d) CUS led to a decrease in action potential firing in dorsal CA1 neurons compared to control group. (e) Representative voltage traces and current injections at −73 mV. (f) The profile of impedance amplitude for voltage traces in e. Vertical lines indicate the resonance frequencies. (g) Resonance frequency was significantly increased in dorsal CA1 neurons following CUS. (h) Representative voltage responses with step current injections at common membrane potential (−73 mV; 750 ms). (i) Bath application of 10 μm ZD7288 showed similar changes in Rin in dorsal CA1 neurons from control and CUS groups. (j) Ih was measured by stepping from a holding potential of −30 mV to −140 mV for 500 ms. (k) Ih was significantly increased in CUS group compared to control group. Data are expressed as mean±s.e.m. with significance indicated by *P<0.05, compared with control group. CUS, chronic unpredictable stress.