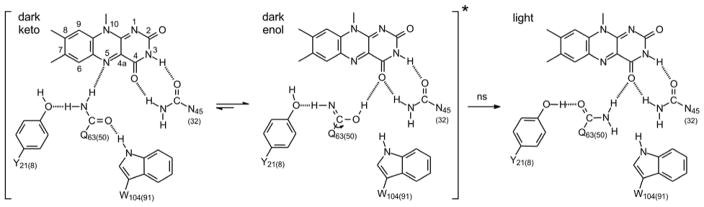
Figure 1. The Hydrogen Bonding Network and Primary Photoactivation Mechanism.
The isoalloxazine ring is surrounded by a conserved hydrogen bonded network that includes a Tyr Y21(8), Gln Q63(50) and Asn N45(32). Also shown is a Trp W104(91) which is shown hydrogen bonded to the Gln residue in the dark state but not in the light state. Movement of the Trp from a Trpin to a Trpout conformation is thought to be a central component of the BLUF photoactivation mechanism although we note that in the X-ray crystal structures of PixD in the dark (PDB: 2HFN)22 and a stable lit states (PDB: 3MZI),7 the W91 sidechain is rotated out of the binding pocket. Photoactivation involves rotation of the Gln side-chain, and in the above mechanism keto-enol tautomerism of the Gln side-chain is shown preceding side-chain rotation.10, 23–25 Residues are numbered based on the sequence of AppA with the residue number in PixD given in parentheses.