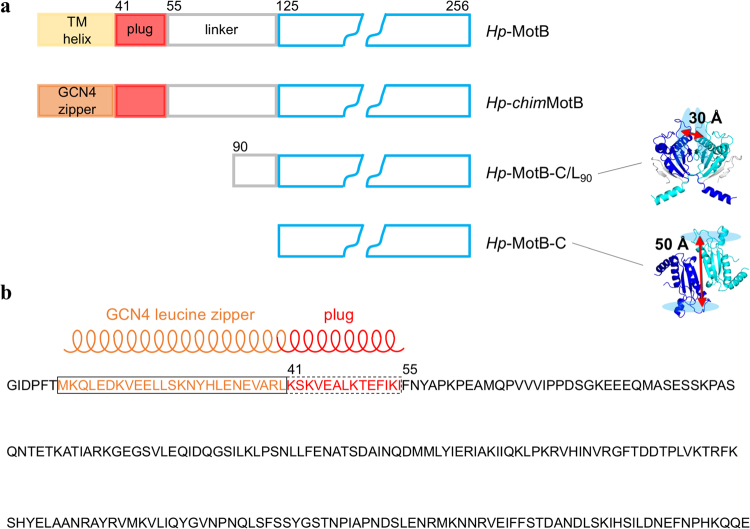
Figure 1.
MotB constructs used in this study. (a) Schematics of native H. pylori MotB and its soluble variants. The peptidoglycan-binding domain is drawn in blue. The crystal structures of the dimers of Hp-MotB-C/L90 23 (PDB ID: 3S0H) and Hp-MotB-C21 (PDB ID: 3CYP) are shown, illustrating the different relative orientation of the two monomers and different spacing between the glycan-binding grooves (shown as light-blue ovals). The residues of the two peptidoglycan-binding domains are coloured blue and cyan; the linker residues in the crystal structure of Hp-MotB-C/L90 are coloured grey. (b) The design of the chimeric variant Hp-chimMotB31 that mimics full-length MotB in its activated (plug as a coiled coil) form. The transmembrane (TM) helix in this chimera is replaced with the GCN4-derived leucine zipper motif; N-terminal GIDPFT is the cloning tag.