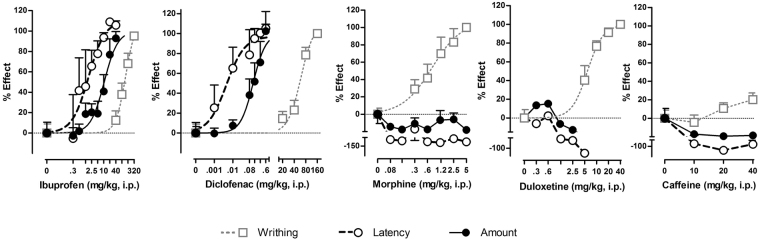
Figure 5.
Comparison of the effect of different drugs on sensory and affective manifestations in AA-induced visceral pain. Dose response curves expressed as % of effect of ibuprofen, diclofenac, morphine, duloxetine and caffeine on two parameters of RSB (latency to eat and amount consumed) and on AA-induced writhing in mice are showed. Drugs were administered to separate groups of mice 90 min after AA to evaluate it effects on RSB changes (30 min before RSB testing) and 30 min before AA to evaluate it effects on writhing response. Ibuprofen and diclofenac displayed more potency to restore RSB (affective) than to reduce writhing behaviour (sensory-reflexive). Both drugs were also more potent in restoring latency to eat (appetitive) as compared to amount consumed (consummatory). Morphine and duloxetine blocked writhing but failed to restore RSB in mice treated with AA. Caffeine, a stimulant non-analgesic drug, lacked activity in any of the behavioural responses evaluated.