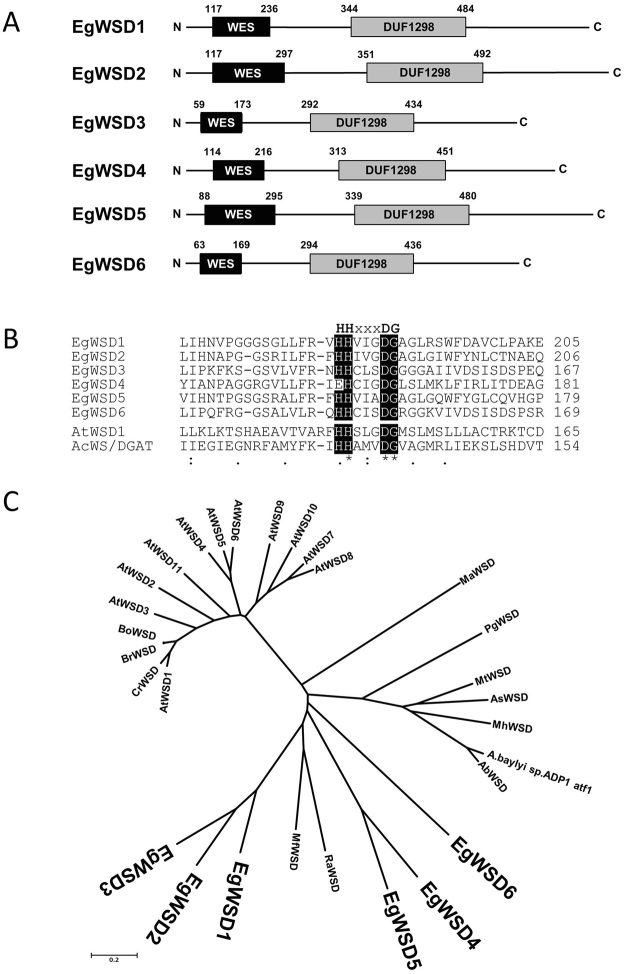
Figure 1.
Primary structure of WSD isoforms in E. gracilis. (A) Molecular organization of six WSD isoforms. Designations of putative domains were based on Pfam domain database: WES, wax ester synthase-like acyl-CoA acyltransferase domain; DUF1298, domain of unknown function. (B) Comparison of putative active site residues of WSDs from Euglena (EgWSD1-6, LC069357-LC069364), Arabidopsis (AtWSD1, At1G72110) and Acinetobacter calcoaceticus ADP1 (AcWS/DGAT, AF529086) using the ClustalW program. Amino acids matching the putative active site motif HHxxxDG are shaded in black. (C) Phylogenetic analysis of the six WSDs from Euglena and proteins related to WSD from other organisms. Phylogenetic trees were constructed with full-length WSD amino acid sequences using the neighbor-joining (NJ) method using the MEGA 6.0 software (http://www.megasoftware.net/). Sequence alignments were assembled by the ClustalW algorithem version 2.1. Abbreviations and UniProt accession numbers except for EgWSDs are as follows: At, Arabidopsis thaliana (AtWSD1-11, Q93ZR6, Q9C7H4, F4IU14, Q9M3B3, Q9M3B2, Q9M3B1, Q94CK0, Q9FFE8, Q9FK89, Q9FK04, Q5KS41); Bo, Brassica oleracea var. oleracea (A0A0D3APY8); Br, Brassica rapa (A0A078CR28); Cr, Capsella rubella (R0IEG2); Ab, Acinetobacter baumannii (A0A077GKS2); As, Amycolicicoccus subflavus DQS3-9A1 (F6EKR7); Mh, Marinobacter hydrocarbonoclasticus (A3RE50); A.baylyi sp.ADP1 aft, Acinetobacter baylyi sp. ADP1(Q8GGG1); Mt, Mycobacterium tuberculosis (P9WKC7); Ra, Rhodococcus aetherivorans (A0A1Q8I8D0); Mf, Myxococcus fulvus 124B02 (A0A0F7DYG7); Ma, Mucor ambiguus (A0A0C9N7W4); Pg, Photobacterium ganghwense (A0A0J1HAU3).