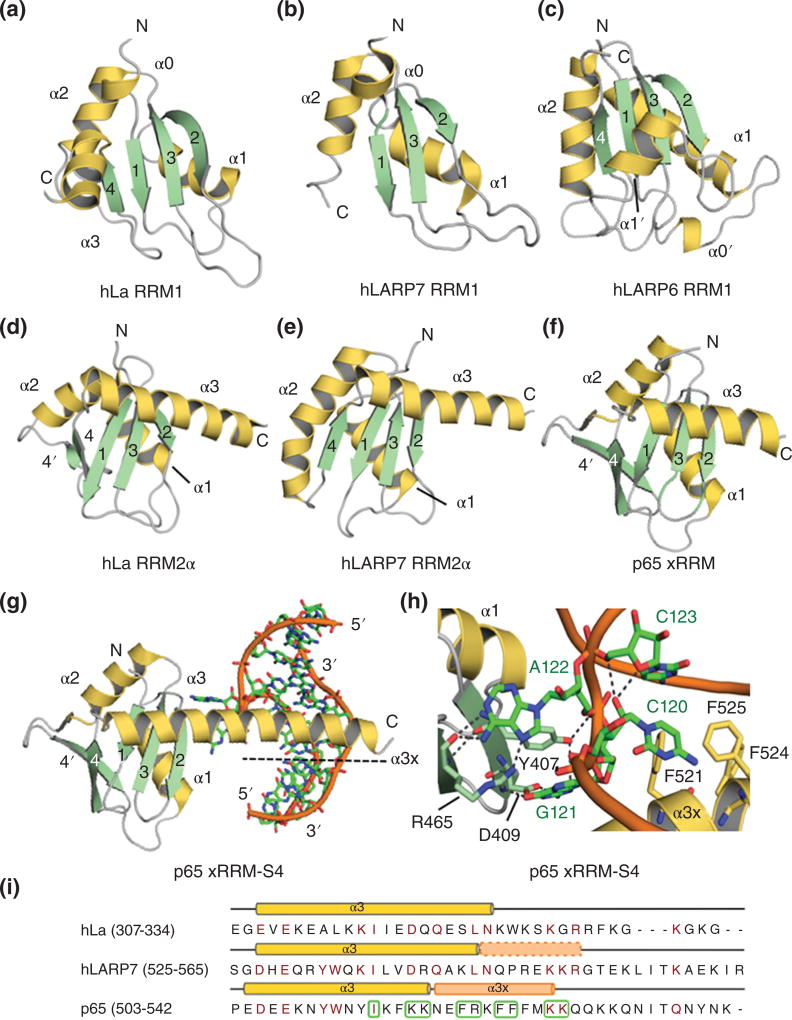
Figure 6. Comparison of RRM1 and RRM2 domains in LARPs.
The RRM1 domains of LARPs are structurally diverse: A) hLa RRM1 (PDB 1S79); B) hLARP7 RRM1 (PDB 4WKR); C) hLARP6 RRM1 (PDB 2MTG). hLARP7 RRM1 lacks strand β4; hLARP6 RRM1 contains additional helices α0’ and α1’. The RRMs2 of D) hLa (PDB 1OWX), E) hLARP7 (PDB 5KNW) and F) p65 (PDB 4EYT) all contain a long C-terminal helix (α3) that obscures the β-sheet platform. G) In p65 the unstructured C-terminal of the helix (α3×) refolds upon RNA binding. H) Close-up view of the interaction between p65 and the S4 RNA. Selected residues are highlighted in stick representation. I) Sequence alignment of the α3 region for hLa, hLARP7 and p65 performed with Clustal Omega in Uniprot portal (http://www.uniprot.org/align/300) and edited and analyzed with Jalview301. Residues colored in dark red indicate conservation. Boxed residues denote amino acids that interact with RNA in p65.