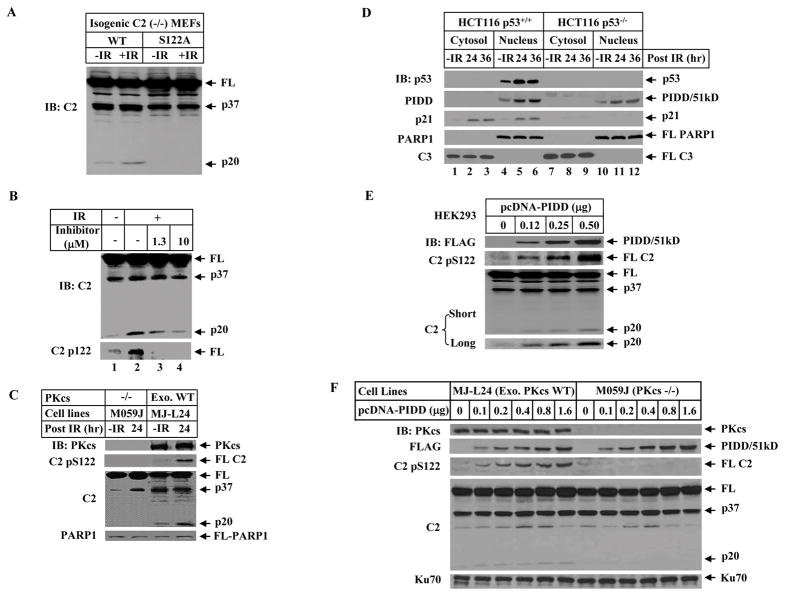
Figure 3. DNA-PKcs Mediates S122 Phosphorylation and Activation of Caspase-2 In Vivo, which Is Facilitated by PIDD.
(A)Phosphorylation site mutation attenuated IR-induced p20 cleavage of caspase-2. The immortalized caspase-2-deficient MEFs stably expressing wild-type or S122A mutant caspase-2 were irradiated (10 Gy for 2 hrs) and nuclear extracts were analyzed by IB.
(B) DNA-PKcs-specific inhibitor blocks caspase-2 phosphorylation at S122 and reduces the p20 cleavage. HeLa cells were incubated for 1 hr with 1.3 μM or 10 μM the inhibitor NU7026 prior to the treatment with 80 Gy. After additional 24 hrs, cells were harvested. Nuclear caspase-2 was detected by IB with caspase-2 antibody and the phosphorylated caspase-2 by an antibody specific for phospho-serine 122 in nuclear extracts.
(C) Caspase-2 phosphorylation at S122 site is abolished in DNA-PKcs-deficient cells. Human glioma M059J (DNA-PKcs-deficient) and isogenenic DNA-PKcs-proficient ML-L24 [with exogenous (exo) wild-type (WT) DNA-PKcs expressed back] cells were exposed to 80 Gy IR. After additional culture for 24 hrs cells were harvested and nuclear extracts were analyzed by IB.
(D)DNA damage induces PIDD accumulation in the cell nucleus. HCT116 p53+/+ and HCT116 p53−/− cells were untreated or exposed to 80 Gy IR, and harvested at 0, 24 or 36 hrs post IR. Cytosolic and nuclear fractions were analyzed by IB.
(E) PIDD overexpression facilitates nuclear caspase-2 phosphorylation and processing. HEK293T cells were transfected with increasing amounts of pcDNA-FLAG-PIDD for 24 hrs. Nuclear extracts were analyzed by IB. The p20 cleavage product of caspase-2 was better illustrated with longer exposure (bottom).
(F) PIDD requires DNA-PKcs to enhance phosphorylation at S122 and nuclear caspase-2 cleavage. pcDNA-FLAG-PIDD was transfected into isogenic ML-L24 and M059J cells for 24 hrs. Nuclear extracts were analyzed by IB.