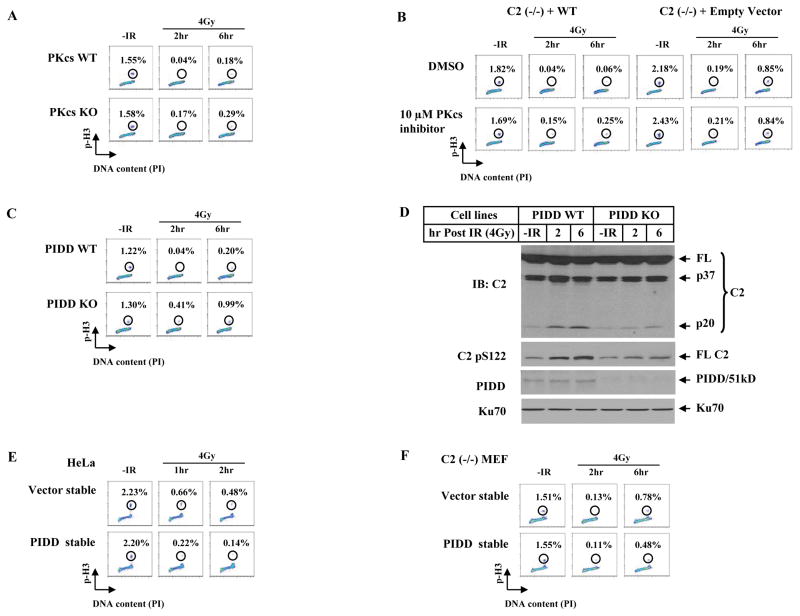
Figure 6. DNA-PKcs and PIDD Affect G2/M DNA Damage Checkpoint.
(A)DNA-PKcs contributes to a G2/M checkpoint. Immortalized wild-type and DNA-PKcs knockout MEF lines were irradiated with 4 Gy, cultured for 2 and 6 hrs, and mitotic percentages were analyzed.
(B) DNA-PKcs kinase inhibitor influences the caspase-2 G2/M checkpoint. Isogenic wild-type and caspase-2-deficient MEF lines were incubated with 10 μM DNA-PKcs inhibitor for 1 hr, irradiated with 4 Gy of IR, and mitotic percentages were analyzed at 2 and 6 hrs post IR.
(C) Endogenous PIDD contributes to a G2/M checkpoint. Isogenic wild-type and PIDD knockout MEF lines were treated and analyzed the same as in A.
(D)Endogenous PIDD is required for a full activation of nuclear caspase-2. Nuclear extracts from PIDD cell lines treated identically as in C were analyzed by IB.
(E) PIDD-overexpression induces a stronger activation of a G2/M checkpoint. HeLa cells stably expressing an empty vector or FLAG-tagged PIDD (PIDD-stable) were exposed to 4 Gy IR, cultured for 1 and 2 hrs, and analyzed for mitotic percentages.
(F) Requirement of caspase-2 for PIDD to activate a G2/M checkpoint. Caspase-2-deficient MEFs [C2 (−/−)] stably expressing an empty vector (Vector-stable) or FLAG-tagged PIDD (PIDD-stable) were exposed to 4 Gy IR, cultured for additional 2 or 6 hrs, and analyzed for mitotic percentages.