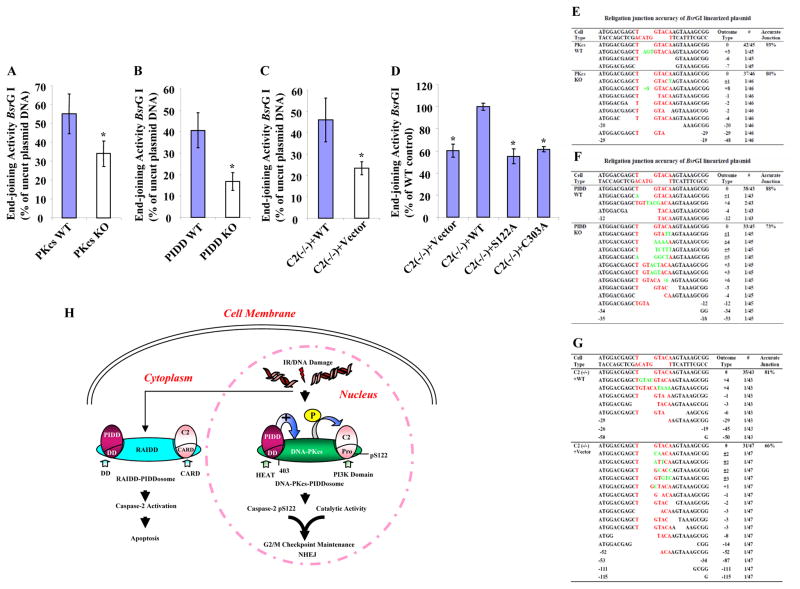
Figure 7. Three Components of DNA-PKcs-PIDDosome Play Roles in NHEJ In Vivo.
(A)DNA-PKcs functions in vivo in DNA end-joining. In vivo plasmid-based end-joining assay using the pEGFP-N1 vector linearized by BsrGI as substrate was performed in immortalized wild type and DNA-PKcs knockout MEF cells. The end-joining activity was estimated as the ratio of the percentage of GFP-positive cells containing recirculized plasmid DNA arising from repair to that of GFP-positive cells transfected with uncut circular plasmid DNA. Each bar represents the mean ±S.D. of three independent experiments (n=3); *, p < 0.05 (two-tailed Student’s t test).
(B) PIDD functions in vivo in DNA end-joining assayed the same as in (A).
(C) Caspase-2 functions in vivo in DNA end-joining assayed as in (A).
(D)Both S122 and C303 sites are required for caspase-2 end-joining activity. The same in vivo end-joining assay as in (A) was performed in the four isogenic caspase-2 cell lines. The end-joining activity in C2 (−/−) + WT cells was arbitrarily set at 100%, which served as a reference and the activities in three other cell lines were normalized to that in C2 (−/−) + WT cells. Each bar represents the mean ±S.D. of three independent experiments (n=3); *, p < 0.05 (two-tailed Student’s t test).
(E) – (G) The junction accuracy frequencies of in vivo DNA end-joining. The relegation junctions of BsrGI restriction site were sequenced. The DNA sequencing results with the exact nucleotides of BsrGI restriction site (red letters) was shown at the top of each set of sequences. The number of times each sequence was represented in the data set was indicated in the column “Outcome Type” as #; also shown in the same column was the nucleotide loss (empty space) from the religation ends as -; the nucleotide addition (green letters) as +; and the nucleotide loss and addition as ±.
(H) Working model for the roles of DNA-PKcs-PIDDosomes in DNA damage-induced cellular responses. In addition to the RAIDD-PIDDosome that is present mainly in cytoplasm to activate caspase-2 for apoptosis, DNA-PKcs-PIDDosome is pre-formed in the cell nucleus without any stimulation. DNA damage (IR) induces nuclear caspase-2 phosphorylation at serine 122 site within its prodomain, and this phosphorylation is mediated by DNA-PKcs, whose kinase activity is facilitated by PIDD, leading to nuclear caspase-2 activation and cleavage. Both this phosphorylation and the catalytic activity of nuclear caspase-2 contribute to G2/M DNA damage checkpoint and NHEJ.