Figure 4.
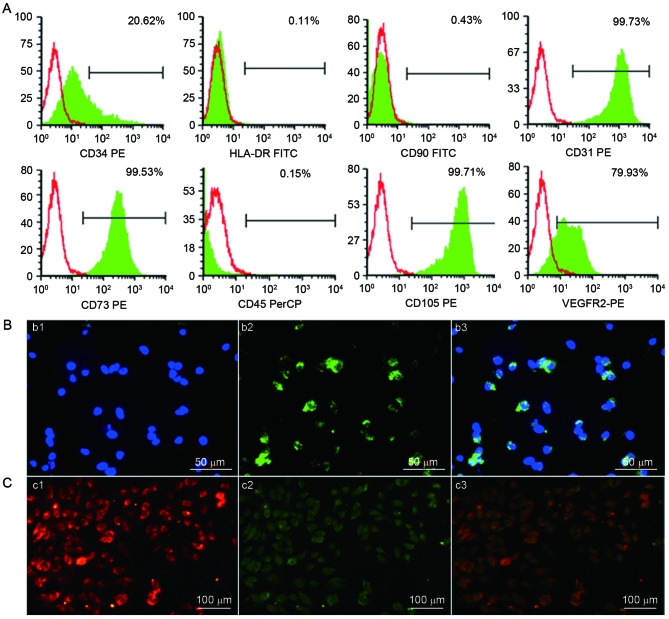
Identification of human UC-ECFCs. (A) Immunophenotype of human UC-ECFCs by FACSCalibur flow cytometry. Human UC-ECFCs were positive for CD31 (99.73%), CD34 (20.62%), CD73 (99.53%), VEGFR-2 (79.93%), CD105 (99.71%) and negative for CD45 (0.15%), CD90 (0.43%) and HLA-DR (0.11%). Filled white histograms represent antigen staining with negative isotype, and the green part represents positive isotype. (B) Human UC-ECFCs expressed the endothelial cell-surface marker vWF. The immunofluorescence detection results demonstrated that the cells could be strained by (b1) DAPI (blue) and (b2) mouse anti-human vWF antibody (green). (b3) Double stained cells (merged b1 and b2) Scale bar, 50 µm. (C) Following 24 h of culture, the adherent cells were identified by the uptake of (c1) 1,1′-dioctadecyl-3,3,3′,3′-tetra-methyl-indocarbocyanine perchlorate-labeled acetylated low-density lipoprotein (red fluorescence) and binding of (c2) FITC-Ulex europaeus lectin-l (green fluorescence). (c3) Double-positive stained cells showed in yellow. Scale bar, 100 µm. UC-ECFCs, umbilical cord-derived endothelial colony-forming cells; CD, cluster of differentiation; HLA-DR, human leukocyte antigen-antigen D related protein; VEGFR, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor; PE, phycoerythrin; FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate; PerCP, peridin-chlorophyll-protein.