Figure 3.
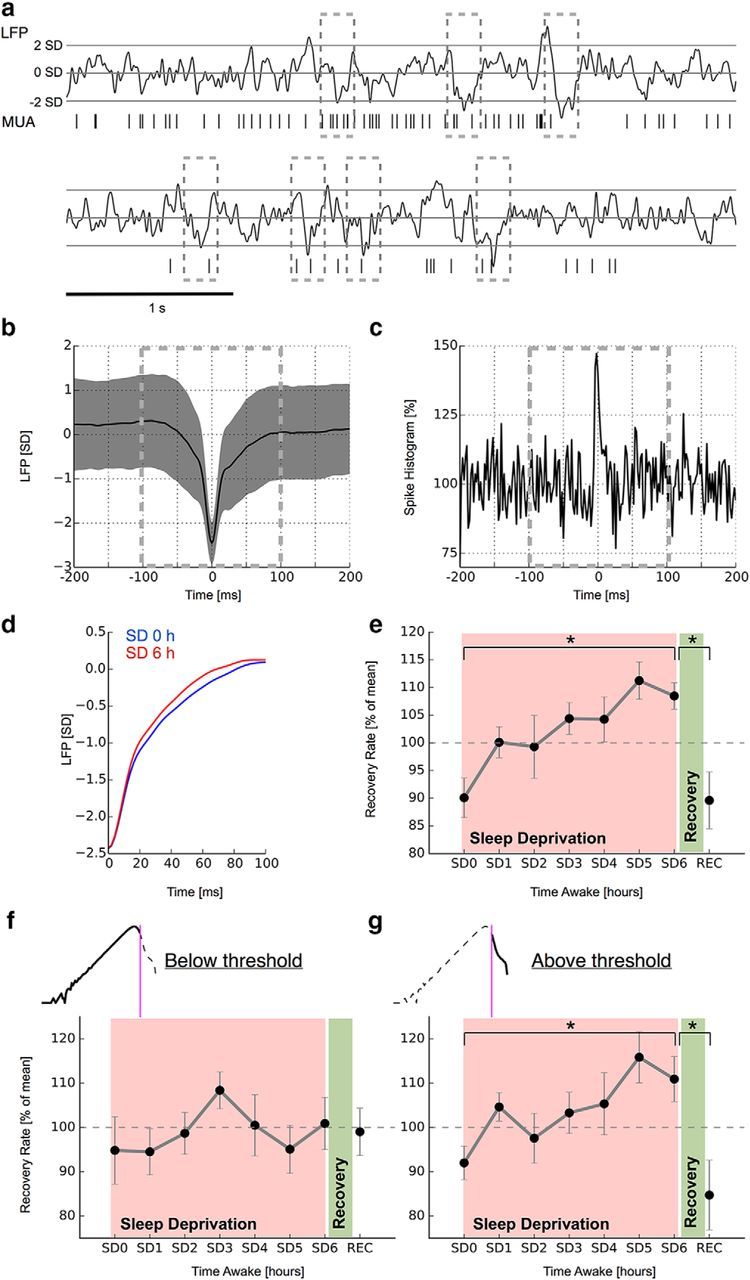
Two-state dynamics underlie the accelerated recovery from large-activity events during sleep deprivation. a, Identification of large-activity events from LFP. nLFP (⩽ 2 SDs) deflections were averaged over each time point during the sleep deprivation experiment (SD0–SD6, REC) and for each rat. b, Mean nLFP over all events and channels (1 rat; SEM). c, Corresponding nLFP-triggered spike histogram. The histogram is normalized to mean activity from −150 to −100 ms. d, Recovery from intrinsic nLFP excursions accelerates as a function of time awake and recovers after sleep. Mean nLFP traces from the beginning and end of sleep deprivation from one rat are shown. e, Summary of nLFP recovery rates for all n = 7 animals (SEM). f, g, More rapid recovery from large-activity events is restricted to data segments containing large-amplitude LFP events. All analyzed data are from dataset 2. ★ indicates a significance value p < 0.05.
