Figure 4.
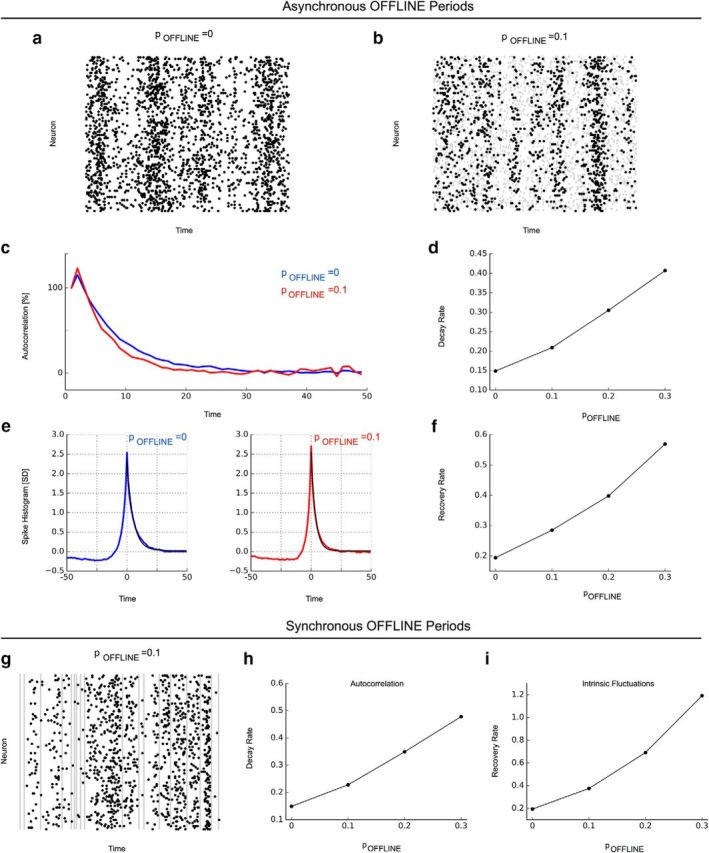
Neuron network model with the ability of neurons to go offline captures the differential decline of long-range temporal correlations. The network was instantiated at a connectivity K = 1 and with different probablities pOFFLINE for neurons to go offline for a brief amount of time in an asynchronous (a–f) or synchronous (g–i) manner. a, Raster plot without the presence of offline periods. b, Raster plot with asynchronous offline periods (pOFFLINE = 0.1, gray shaded areas). c, Autocorrelation functions for spiking activity in a network without offline periods (pOFFLINE = 0, blue) and in a network with asynchronous offline periods (pOFFLINE = 0.1, red) in neuron activity. d, Autocorrelation decay rates increase with higher probability for asynchronous offline periods. e, Recovery from intrinsic fluctuations (pOFFLINE = 0, blue; pOFFLINE = 0.1, red). f, Recovery rates from intrinsic fluctuations increase with higher probability for asynchrnous offline periods. g, Raster plot with synchronous offline periods (gray shaded areas). h, i, Autocorrelation decay and recovery rates from intrinsic fluctuations increase with higher probability for synchronous offline periods.
