Figure 6.
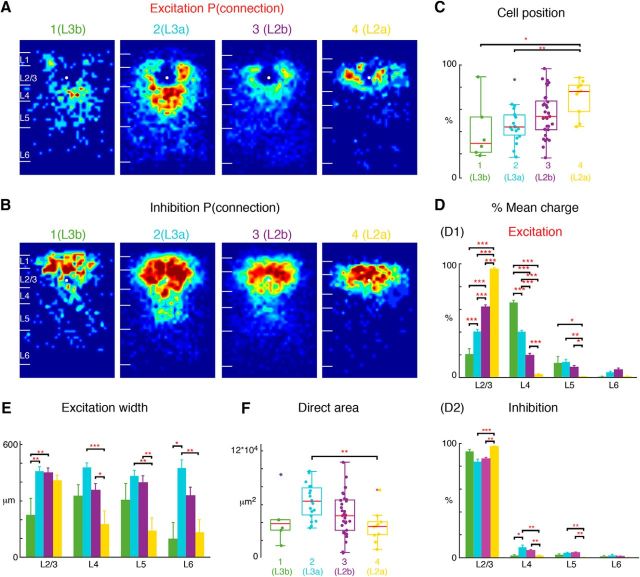
L3 also subdivides into two sublayers: L3a, L3b. L3 can also be divided into two groups representing L3b (Group 1) and L3a (Group 2). With the prior two subgroups in L2 (Group 3: L2b and Group 4: L2a; same as Fig. 5) we have divided L2/3 cells into 4 groups. A, Average maps (aligned to soma, white circle) of connection probability for excitatory connections among four groups of cells. Connection probability is encoded according to the pseudocolor scale. White horizontal lines indicate averaged laminar borders and are 100 μm long. B, Average maps (aligned to soma, white circle) of connection probability for inhibitory connections among four groups of cells. Connection probability is encoded according to the pseudocolor scale. White horizontal lines indicate averaged laminar borders and are 100 μm long. C, Boxplot of relative cell positions of Group 1 (L3b; green), Group 2 (L3a; light blue), Group 3 (L2b; purple), and Group 4 (L2a; yellow) cells within L2/3. The locations of L2a cells are close to the upper boundary of L2/3 and the locations of L3b cells are close to the lower boundary of L2/3. The cell location of L3a and L2b are in between. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. The p values from multiple-comparison test are as follows: L3b vs L3a: p = 0.89; L3b vs L2b: p = 0.27; L3b vs L2a: p = 0.012; L3a vs L2b: p = 0.35; L3a vs L2a: p = 7.89 × 10−3; L2b vs L2a: p = 0.12. D, Layer-specific fractional excitatory (D1) and inhibitory (D2) charge of L3b, L3a, L2b, and L2a cells. Data are mean charge ± SEM. Comparing the excitation originating from L2/3 or L4 between groups shows differences. The main input to L3b cells come from L4, whereas the main input to L2a is within L2/3. L3a and L2b have most input both coming from L2/3 and L4. The p values from multiple-comparison test are as follows: L2/3: L3b vs L3a: p = 6.32 × 10−5; L3b vs L2b: p = 3.77 × 10−9; L3b vs L2a: p = 3.77 × 10−9; L3a vs L2b: p = 3.81 × 10−9; L3a vs L2a: p = 3.77 × 10−9; L2b vs L2a: p = 3.77 × 10−9. L4: L3b vs L3a: p = 8.60 × 10−8; L3b vs L2b: p = 3.77 × 10−9; L3b vs L2a: p = 3.77 × 10−9; L3a vs L2b: p = 3.78 × 10−9; L3a vs L2a: p = 3.77 × 10−9; L2b vs L2a: p = 3.44 × 10−6. L5: L3b vs L3a: p = 0.99; L3b vs L2b: p = 0.76; L3b vs L2a: p = 4.33 × 10−2; L3a vs L2b: p = 0.25; L3a vs L2a: p = 1.63 × 10−3; L2b vs L2a: p = 4.75 × 10−2. L6: L3b vs L3a: p = 0.54; L3b vs L2b: p = 0.14; L3b vs L2a: p = 0.99; L3a vs L2b: p = 0.63; L3a vs L2a: p = 0.41; L2b vs L2a: p = 0.051. Inhibition also shows some difference among four groups. The p values from multiple-comparison tests of inhibition are as follows: L2/3: L3b vs L3a: p = 7.35 × 10−2; L3b vs L2b: p = 0.24; L3b vs L2a: p = 0.69; L3a vs L2b: p = 0.69; L3a vs L2a: p = 2.30 × 10−4; L2a vs L2b: p = 1.34 × 10−3. L4: L3b vs L3a: p = 4.02 × 10−2; L3b vs L2b: p = 0.32; L3b vs L2a: p = 0.99; L3a vs L2b: p = 0.29; L3a vs L2a: p = 5.07 × 10−3; L2a vs L2b: p = 4.94 × 10−3. L5: L3b vs L3a: p = 0.61; L3b vs L2b: p = 0.52; L3b vs L2a: p = 0.47; L3a vs L2b: p = 0.99; L3a vs L2a: p = 6.25 × 10−3; L2a vs L2b: p = 1.98 × 10−3. L6: L3b vs L3a: p = 0.85; L3b vs L2b: p = 0.99; L3b vs L2a: p = 0.78; L3a vs L2b: p = 0.44; L3a vs L2a: p = 0.13; L2a vs L2b: p = 0.64. E, Barplot of the distance of 80% of input to each L2/3 cell originating from L2/3, L4, L5, and L6. The p values from multiple-comparison test are as follows: L2/3: L3b vs L3a: p = 2.60 × 10−3; L3b vs L2b: p = 2.15 × 10−3; L3b vs L2a: p = 5.27 × 10−2; L3a vs L2b: p = 0.99; L3a vs L2a: p = 0.77; L2a vs L2b: p = 0.85. L4: L3b vs L3a: p = 0.28; L3b vs L2b: p = 0.98; L3b vs L2a: p = 0.37; L3a vs L2b: p = 0.10; L3a vs L2a: p = 3.40 × 10−4; L2a vs L2b: p = 3.42 × 10−2. L5: L3b vs L3a: p = 0.51; L3b vs L2b: p = 0.72; L3b vs L2a: p = 0.38; L3a vs L2b: p = 0.92; L3a vs L2a: p = 1.82 × 10−3; L2a vs L2b: p = 3.41 × 10−3. L6: L3b vs L3a: p = 0.011; L3b vs L2b: p = 0.14; L3b vs L2a: p = 0.97; L3a vs L2b: p = 0.31; L3a vs L2a: p = 9.80 × 10−3; L2a vs L2b: p = 0.19. F, Boxplot of the direct activation area of L3b, L3a, L2b, and L2a cells. L3a (light blue) cells have bigger direct activation area than L2a cells (yellow; p = 8.0 × 10−3). There is no difference between L3b, L2b, and L2a (L3b vs L2b: p = 0.93; L3b vs L2a: p = 0.89; L2a vs L2b: p = 0.30). Triple asterisk indicates a higher significance level.