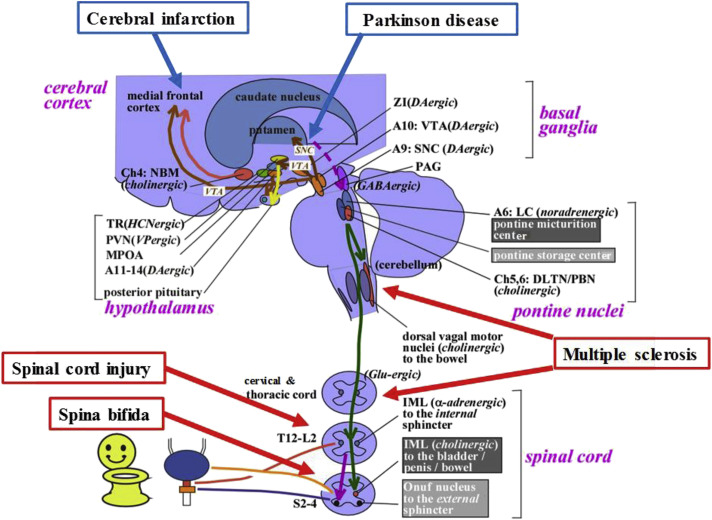
Fig. 4.
Neural circuitry relevant to micturition. The lower urinary tract consists of 2 major components: the bladder, and the urethra. The bladder is mainly innervated by the parasympathetic pelvic nerve. The urethra is innervated by the sympathetic hypogastric nerve and somatic pudendal nerve, respectively. Urinary storage depends on the reflex arc of the sacral spinal cord. The storage reflex is thought to be tonically facilitated by the brain, particularly the pontine storage center. The storage function is thought to be further facilitated by the hypothalamus, cerebellum, basal ganglia, and frontal cortex. Central cholinergic fibers from the nucleus basalis Meynert (NBM; also called the Ch4 cell group) seem to facilitate urinary storage. Micturition depends on the reflex arc of the brainstem and spinal cord, which involves the midbrain PAG and the PMC (located in or adjacent to the locus coeruleus [LC]). The voiding function is thought to be initiated by the hypothalamus and prefrontal cortex, which overlap the storage-facilitating area. CI induces the neural damage in the cerebrum. PD is primarily induced by degeneration of dopaminergic (DAgic) neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNC). MS is induced by focal demyelization of the central nervous system at various levels. SCI is induced by complete or incomplete neural damages of the spinal cord at different levels. Spina bifida is caused by a failure of the caudal neural tube to fuse normally in early development, thus often inducing the damage of the lumbosacral spinal cord and resulting in myelomeningocele, in which the spinal cord and neural elements are exposed. A, adrenergic or noradrenergic; DLTN, dorsolateral tegmental nucleus; GABA, γ-aminobutyric acid; HCN, hypocretinergic; IML, intermediolateral cell column; L, lumbar; MPOA, medial preoptic area; PBN, parabrachial nucleus; PVN, paraventricular nucleus; S, sacral; SNC, substantia nigra pars compacta; T, thoracic; TR, tuberous region; VTA, ventral tegmental area; ZI, zona incerta.