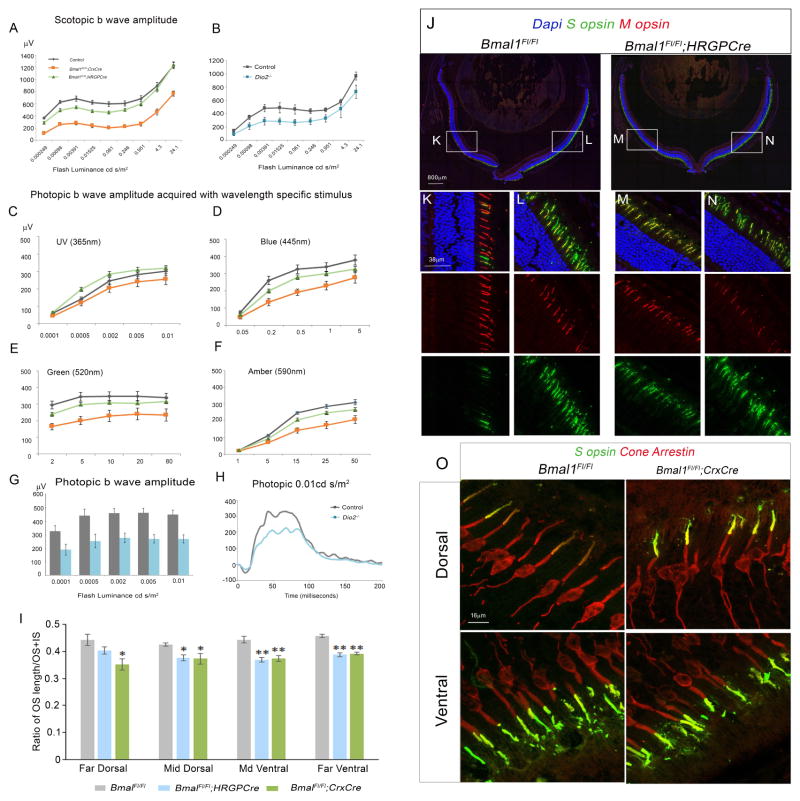
Figure 7. Bmal1 and Dio2 are required for adult cone function and maintenance.
(A–B) Dark-adapted b-wave responses were decreased in 6 weeks old Bmal1 CKO (A) and Dio2−/−mutants (B) compared to the reponses recorded from the respective littermate controls.
(C–F) Light adapted ERG b-wave responses in 6 weeks old Bmal1 CKO and littermate control mice using 365 nm (C), 445 nm (D), 520 nm (E) and 590 nm (F) of light sources. (C) b-wave responses at 365 nm were significantly higher in the HRGP-Cre; Bmal1Fl/Fl group (F2, 65=18.74; P<0.001). (D–F) b-wave responses at 445 nm (F2, 65=35.25; P<0.001), 520 nm (F2, 65=41.08; P<0.001) and 590 nm (F2, 65=40.36; P<0.001) were significantly lower in both Bmal1 conditional mutant groups compared to the control group.
(G–H) Light-adapted b-wave responses were significantly decreased in Dio2 mutants at 6 weeks of age. Error bars are ± SEM and n=4–8. Results were analyzed using two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post-hoc test with genotype and flash intensity as two independent factors.
(J–N) Dorsal and ventral retinal sections from 3 month old control animal (K and L,) and Bmal1 CKO (M and N,) labeled with S opsin (green) and M opsin (red). (O) Dorsal and ventral retinal sections from 3 month old control animal and Bmal1 CKO labeled with S opsin (green) and Cone arrestin (red). (I) Quantification of cone outer segment length (OS). The cones from Bmal1 CKO retina have shorter OS compared to littermate controls suggesting a role for Bmal1 in maintenance of the photoreceptors. Results were analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post-hoc test.* indicates P<0.05 and ** indicates P<0.01.