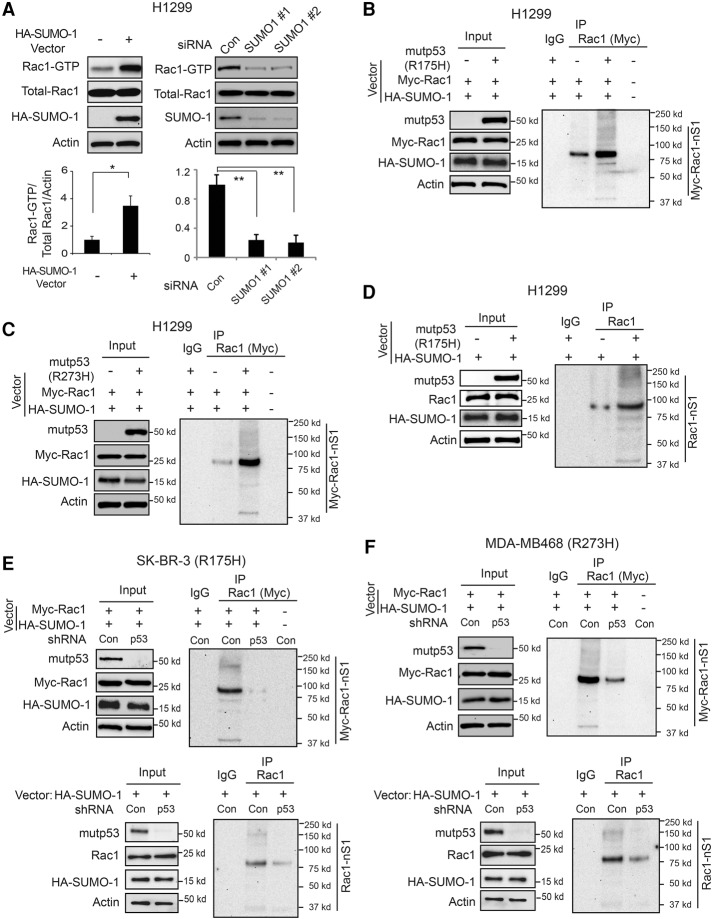
Figure 4.
Mutant p53 increases Rac1 SUMOylation levels in human cancer cells. (A) SUMOylation increased Rac1 activity in H1299 cells. (Left panels) Ectopic expression of HA-SUMO-1 in H1299 cells increased the levels of Rac1-GTP. (Right panels) Knockdown of endogenous SUMO-1 by two different siRNA oligos decreased the levels of Rac1-GTP. (Top panels) Representative Western blot images for Rac1 activity analysis. (Bottom panels) Quantitation of relative Rac1-GTP/total Rac1/Actin levels. Data are presented as mean ± SD. n = 3. (*) P < 0.01; (**) P < 0.001, Student's t-test. (B,C) Ectopic mutant p53 (R175H in B and R273H in C) increased SUMOylation levels of Myc-Rac1 in H1299 cells. H1299 cells were transfected with expression vectors of mutant p53 (R175H and R273H, respectively), Myc-Rac1, and HA-SUMO-1. The Myc-Rac1 SUMOylation levels were determined by Myc-Rac1 pull-down using an anti-Myc antibody followed by Western blot assays using an anti-HA antibody. (D) Mutant p53 (R175H) increased SUMOylaiton levels of endogenous Rac1 in H1299 cells. (E,F) Knockdown of endogenous mutant p53 in SK-BR-3 (E) and MDA-MB468 (F) cells, respectively, decreased SUMOylation levels of both ectopic Myc-Rac1 (top panels) and endogenous Rac1 (bottom panels). SK-BR-3 and MDA-MB468 cells with or without endogenous mutant p53 knockdown were transfected with expression vectors of HA-SUMO-1 along with or without Myc-Rac1.